Recent Update on Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension: Based on the 2023 European Society of Hypertension Guidelines
- Min Kyoung Kang, MD, PhD
кі нҳҲм••мқҳ 진лӢЁ л°Ҹ м№ҳлЈҢ: 2023 мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқёмқ„ кё°л°ҳмңјлЎң
- к°•лҜјкІҪ
- Received February 22, 2024; В В В Revised June 7, 2024; В В В Accepted June 13, 2024;
- ABSTRACT
-
Since the release of the updated hypertension guidelines by the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and American Society of Hypertension, noteworthy revisions have been introduced by both the Korean Society of Hypertension and the European Society of Hypertension. Given the increasing prevalence of hypertension, it is essential for neurologists who frequently encounter patients with multiple chronic condition to have a thorough understanding of hypertension. In addition, effectively controlling hypertension can potentially lower the risk of neurological disorders including stroke and cognitive impairment. Thus, itвҖҷs crucial for neurologists and healthcare professionals to possess a comprehensive understanding of diagnosing and managing hypertension. Therefore, in this paper, the essentials for the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension based on the latest guidelines from the European Society of Hypertension are summarized.
- м„ң лЎ
- м„ң лЎ
кі нҳҲм••мқҖ мҡ°лҰ¬лӮҳлқј м„ұмқё мқёкө¬ 3лӘ… мӨ‘ 1лӘ…мқё 1,200л§Ң лӘ…мқҙ ліҙмң н•ң лҢҖн‘ңм Ғмқё көӯлҜј л§Ңм„ұ м§ҲнҷҳмқҙлӢӨ[1]. кі нҳҲм••мқҖ м„ұмқёмқҳ мӮ¬л§қ мӣҗмқё мӨ‘ к°ҖмһҘ мЈјмҡ”н•ң мң„н—ҳ мҡ”мқёмқё мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳкіј л°Җм ‘н•ң кҙҖл Ёмқҙ мһҲкі м Ғм ҲнһҲ м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ лҗңлӢӨл©ҙ к·ёлЎң мқён•ң мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖ н•©лі‘мҰқ л°Ҹ мӮ¬л§қ мң„н—ҳмқ„ к°җмҶҢмӢңнӮ¬ мҲҳ мһҲлҠ” мЎ°м Ҳ к°ҖлҠҘн•ң мң„н—ҳмқёмһҗлқјлҠ” м җм—җм„ң мӨ‘мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ[2]. көӯлӮҙмқҳ кі нҳҲм•• мЎ°м ҲлҘ мқҖ л№ лҘё 추세лЎң мғҒмҠ№ мӨ‘мқҙлӮҳ мң лі‘лҘ мқҖ м—¬м „нһҲ мҰқк°Җ 추세мқҙл©° кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗмқҳ кІҪмҡ° лҮҢмЎёмӨ‘ л°Ҹ мқём§ҖмһҘм• л“ұмқҳ мӢ кІҪкі„м§Ҳнҷҳмқ„ лҸҷл°ҳн•ҳлҠ” кІҪмҡ°к°Җ л§ҺмңјлҜҖлЎң мӢ кІҪкіј мқҳлЈҢ진мқҳ кі нҳҲм•• 진лӢЁ л°Ҹ кҙҖлҰ¬м—җ лҢҖн•ң мҲҷм§Җк°Җ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ[3,4]. 2022л…„ лҢҖн•ңкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢм—җм„ң көӯлӮҙ мӢӨм •м—җ л§һлҠ” кі нҳҲм•• 진лӢЁ л°Ҹ м№ҳлЈҢм§Җм№Ёмқ„ л°ңн‘ңн•ҳмҳҖмңјл©° мқҙнӣ„ 2023л…„ мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқёмқҙ к°ңм •лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ. ліё л…јл¬ём—җм„ңлҠ” 2023л…„ мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқё к°ңм •м•Ҳмқ„ мӨ‘мӢ¬мңјлЎң көӯлӮҙ м„ұмқём—җм„ңмқҳ м •нҷ•н•ң кі нҳҲм•• 진лӢЁ л°Ҹ м Ғм Ҳн•ң м№ҳлЈҢм—җ лҢҖн•ҳм—¬ мӮҙнҺҙліҙкі мһҗ н•ңлӢӨ[5,6].
- ліё л¬ё
- ліё л¬ё
- 1. кі нҳҲм••мқҳ м •мқҳ
- 1. кі нҳҲм••мқҳ м •мқҳ
нҳ„мһ¬к№Ңм§Җмқҳ мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳ мҳҲл°©м—җ кҙҖн•ң мһ„мғҒ м—°кө¬ кІ°кіјлҘј л°”нғ•мңјлЎң 140/90 mmHg мқҙмғҒмқ„ кі нҳҲм••мқҙлқјкі көӯм ңм ҒмңјлЎң м •мқҳн•ҳкі мһҲлӢӨ(Table 1) [2,7,8]. м •мғҒ нҳҲм••мқҖ мҲҳ축기нҳҲм•• 120 mmHg лҜёл§Ңмқҙл©ҙм„ң нҷ•мһҘкё°нҳҲм•• 80 mmHgлҘј лӘЁл‘җ л§ҢмЎұн•ҳлҠ” кІҪмҡ°лҘј лң»н•ҳл©° мһ„мғҒм ҒмңјлЎң мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖ мң„н—ҳлҸ„к°Җ лӮ®мқҖ нҳҲм••кө°мқҙлқјлҠ” мқҳлҜёлҘј к°–лҠ”лӢӨ. 2017л…„ лҜёкөӯкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ 진лЈҢм§Җм№Ём—җм„ң кі нҳҲм••мқ„ 130/80 mmHg мқҙмғҒмңјлЎң м •мқҳн•ҳл©ҙм„ң кі нҳҲм•• м •мқҳм—җ лҢҖн•ң л…јлһҖмқҙ мһҲм—ҲмңјлӮҳ лҜёкөӯмӢ¬мһҘнҸҗмғүм „м—°кө¬мӣҗмқҳ кі нҳҲм•• к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқёмқё Joint National Committee 7 к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқё, 2022 лҢҖн•ңкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ 진лЈҢм§Җм№Ё л°Ҹ 2023 мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқёмқҳ кІҪмҡ° кё°мЎҙмқҳ 140/90 mmHg мқҙмғҒмқ„ кі нҳҲм••мңјлЎң м •мқҳн•ҳлҠ” кё°мӨҖмқ„ мң м§Җн•ҳкі мһҲлӢӨ[5,6,9,10]. 2023 мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқём—җм„ңлҠ” кі нҳҲм••мқҳ м •мқҳм—җлҠ” ліҖнҷ”к°Җ м—ҶмңјлӮҳ нҳҲм•• мҲҳм№ҳм—җ к·јкұ°н•ҳм—¬ кі нҳҲм••мқҳ л“ұкёү(grade)мқ„ лӮҳлҲ„кі кі нҳҲм•• м—°кҙҖ мһҘкё° мҶҗмғҒмқ„ кі л Өн•ң лӢЁкі„(stage)лҘј кө¬л¶„н•ҳм—¬ мҡ©м–ҙлҘј м •лҰ¬н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ(Table 2, Fig. 1). кі нҳҲм•• лӢЁкі„мқҳ мғҒм„ё кё°мӨҖкіј мқҳлҜём—җ лҢҖн•ҳм—¬лҠ” н•ҳкё° кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗмқҳ нҸүк°Җм—җм„ң м„ңмҲ н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.- 2. нҳҲм••мқҳ мёЎм •
- 2. нҳҲм••мқҳ мёЎм •
кі нҳҲм••мқҳ 진лӢЁ, м№ҳлЈҢ, мҳҲнӣ„ нҸүк°Җм—җ мһҲм–ҙм„ң к°ҖмһҘ к·јк°„мқҙ лҗҳлҠ” кІғмқҖ м •нҷ•н•ң нҳҲм••мқҳ мёЎм •мқҙлӢӨ. нҳҲм••мқҖ мёЎм • нҷҳкІҪ, мёЎм • кё°кё°, мёЎм • л°©лІ•, нҳҲм•• мёЎм • мЎ°мӮ¬мӣҗмқҳ мҲ кё°м—җ л”°лқјм„ң ліҖлҸҷм„ұмқҙ нҒ¬кё° л•Ңл¬ём—җ м»Өн”„лҘј мӮ¬мҡ©н•ң мғҒмҷ„ мһҗлҸҷ нҳҲм••кі„лҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ н‘ңмӨҖм Ғмқё л°©лІ•мңјлЎң л°ҳліө мёЎм •н•ң 진лЈҢмӢӨ мҲҳ축기нҳҲм•• вүҘ140 mmHg лҳҗлҠ” нҷ•мһҘкё°нҳҲм•• вүҘ90 mmHgлҘј кё°мӨҖмңјлЎң мӮјмңјл©° мқҙ мҷём—җ нҷңлҸҷнҳҲм•• мёЎм • лҳҗлҠ” к°Җм •нҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқ„ л¶Җк°Җм ҒмңјлЎң мӢңн–үн•ҳм—¬ кі нҳҲм••мқ„ 진лӢЁн•ҳкі л¶„лҘҳн•ңлӢӨ[6,9,11,12]. мёЎм • л°©лІ•м—җ л”°лҘё кё°мӨҖмқҙ лӢӨлҘё м җм—җ лҢҖн•ң мҲҷм§Җк°Җ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ(Table 1). мөңк·ј к°ңл°ңлҗҳм–ҙ л„җлҰ¬ мӮ¬мҡ©лҗҳлҠ” мҠӨл§ҲнҠёнҸ° л°Ҹ мҶҢнҳ• кё°кё°лҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ң м»Өн”„ м—ҶлҠ” нҳҲм••кі„лЎң нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ 진лЈҢмӢӨ л°– нҳҲм•• мёЎм •м—җ лҸ„мӣҖмқ„ л°ӣкі мһҲлҠ” л¶Җ분мқҙ мһҲмңјлӮҳ нҳҲм••мқҳ 진лӢЁм—җлҠ” мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ” кІғмқ„ к¶Ңкі н•ҳкі мһҲлӢӨ[13].мІҳмқҢ лі‘мӣҗм—җ л°©л¬ён•ҳлҠ” нҷҳмһҗмқҳ нҳҲм••мқ„ мёЎм •н• л•Ңм—җлҠ” м–‘нҢ”мқҳ нҳҲм••мқ„ лӘЁл‘җ мёЎм •н•ҳл©° лӢӨмқҢм—җлҠ” нҳҲм•• мҲҳм№ҳк°Җ лҶ’мқҖ нҢ”м—җм„ң нҳҲм••мқ„ мёЎм •н•ңлӢӨ. 1분 к°„кІ©мқ„ л‘җкі м Ғм–ҙлҸ„ 2нҡҢ мқҙмғҒ нҳҲм••мқ„ мёЎм •н•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ кё°ліёмқҙл©° л¶Җм •л§Ҙмқҙ мһҲлҠ” кІҪмҡ° 3нҡҢ мқҙмғҒ мёЎм •н•ҳм—¬ нҸүк· мқ„ лӮёлӢӨ[9]. нҳҲм••мқ„ мёЎм •н• л•Ңм—җлҠ” л“ұл°ӣмқҙк°Җ мһҲлҠ” мқҳмһҗм—җ л“ұмқ„ кё°лҢҖм–ҙ м•үлҸ„лЎқ н•ҳкі м–‘л°ңмқ„ нҸүм§Җ мң„м—җ лӮҙлҰ¬кі лӢӨлҰ¬лҘј кј¬м§Җ л§җм•„м•ј н•ҳл©° мң„нҢ”мқҖ мӢ¬мһҘ лҶ’мқҙм—җ мң„м№ҳмӢңмјңм•ј н•ңлӢӨ. мөңмҶҢн•ң 5분간 м•Ҳм •лҗң мғҒнғңлҘј м·Ён•ң лӢӨмқҢм—җ м»Өн”„лҘј мӢ¬мһҘ лҶ’мқҙм—җ мң„м№ҳмӢңмјң нҳҲм••мқ„ мёЎм •н•ңлӢӨ[11,14]. м»Өн”„лҠ” нҢ” л‘ҳл Ҳм—җ м Ғм Ҳн•ң м»Өн”„лҘј мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳм—¬м•ј н•ҳл©° л§Ңм•Ҫ м Ғм • нҒ¬кё°ліҙлӢӨ мһ‘мқҖ нҒ¬кё°мқҳ м»Өн”„лҘј мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳм—¬ мёЎм •н•ҳл©ҙ нҳҲм••мқҙ лҶ’кІҢ мёЎм •лҗңлӢӨ. лҢҖл¶Җ분мқҳ м»Өн”„м—җлҠ” м Ғмҡ© к°ҖлҠҘн•ң нҢ” л‘ҳл Ҳмқҳ лІ”мң„к°Җ н‘ңмӢңлҗҳм–ҙ мһҲм–ҙм„ң нҢ”м—җ л‘ҳлҹ¬ліҙкі м Ғн•©н•ңм§ҖлҘј мңЎм•ҲмңјлЎң нҷ•мқён•ҳлҠ” кІғлҸ„ лҸ„мӣҖмқҙ лҗҳл©° 진лЈҢмӢӨм—җ 3-4к°ң м •лҸ„ мӮ¬мқҙмҰҲмқҳ м»Өн”„лҘј кө¬л№„н•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ лӢӨм–‘н•ң м—°л №лҢҖмҷҖ мІҙнҳ•мқҳ нҷҳмһҗмқҳ нҳҲм••мқ„ мёЎм •н•ҳлҠ” лҚ° лҸ„мӣҖмқҙ лҗ мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. мҲҳ축기нҳҲм•• 180 mmHg, нҷ•мһҘкё°нҳҲм•• 110 mmHg мқҙмғҒмқҳ 3лҸ„ кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗлҘј м ңмҷён•ҳл©ҙ кі нҳҲм••мқ„ 진лӢЁн•ҳкё° мң„н•ҙм„ңлҠ” мғҒкё° кё°мҲ н•ң нҳҲм••мқҳ н‘ңмӨҖ мёЎм •лІ•мқ„ мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳм—¬ 4мЈј мқҙлӮҙ 2нҡҢ мқҙмғҒмқҳ мҷёлһҳ л°©л¬ё мӢңмқҳ нҳҲм•• мёЎм •к°’мқ„ мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳм—¬ нҢҗлӢЁн• кІғмқҙ к¶Ңкі лҗңлӢӨ.진лЈҢмӢӨм—җм„ңмқҳ нҳҲм•• мёЎм • мҷё нҷңлҸҷнҳҲм•• мёЎм • нҳ№мқҖ нҷҳмһҗк°Җ м§Ғм ‘ мӢңн–үн• мҲҳ мһҲлҠ” к°Җм •нҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқҖ 진лЈҢмӢӨм—җм„ң мёЎм •лҗң нҳҲм••ліҙлӢӨ мҳҲнӣ„лҘј лҚ” мһҳ л°ҳмҳҒн•ңлӢӨкі м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲлӢӨ[15-18]. 2023 мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқём—җм„ңлҸ„ 진лЈҢмӢӨ л°– нҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқҳ мӨ‘мҡ”м„ұм—җ лҢҖн•ҳм—¬ к°•мЎ°н•ҳкі мһҲлӢӨ. к°Җм •нҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқҖ кІҖмҰқлҗң мһҗлҸҷ нҳҲм••кі„лҘј мқҙмҡ©н•ҳм—¬ мң„м—җ кё°мҲ н•ң н‘ңмӨҖ нҳҲм•• мёЎм •лІ•мңјлЎң 2нҡҢ мёЎм •н•ңлӢӨ. нҷҳмһҗм—җкІҢ м•„м№Ё кё°мғҒ нӣ„ 1мӢңк°„ мқҙлӮҙ, мҶҢліҖмқ„ ліё нӣ„, кі нҳҲм•• м•Ҫмқ„ ліөмҡ©н•ҳкё° м „м—җ 1нҡҢ мёЎм •н•ҳкі м Җл…Ғ мһ мһҗлҰ¬м—җ л“Өкё° м „м—җ 1нҡҢ мёЎм •н•ҳлҸ„лЎқ мӢңк°„м—җ лҢҖн•ң м§Җм№Ёмқ„ мӨ„ мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. к°Җм •нҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқ„ нҶөн•ҙ мІҳмқҢ кі нҳҲм••мқ„ 진лӢЁн• л•Ңм—җлҠ” м Ғм–ҙлҸ„ мҷёлһҳ л°©л¬ё м „ 7мқјмқҖ кјӯ нҳҲм••мқ„ мёЎм •н•ҳлҸ„лЎқ к¶Ңкі н•ҳкі мөңмҶҢ 3мқј мқҙмғҒмқҳ мёЎм •мқҖ л°ҳл“ңмӢң н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ. к°Җм •нҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқҖ н•„мҡ” 비мҡ©мқҙ лӮ®кі л°ұмқҳкі нҳҲм••мқ„ к°җлі„н• мҲҳ мһҲмңјл©° кёҙмһҘлҗҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ” мғҒнҷ©м—җм„ң л°ҳліөм ҒмңјлЎң мһҘкё°м Ғ нҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқҙ к°ҖлҠҘн•ң мһҘм җмқҙ мһҲмңјлӮҳ мёЎм •лІ•м—җ лҢҖн•ң м§Җм№Ёмқ„ лҜёлҰ¬ көҗмңЎн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ[19,20].нҷңлҸҷнҳҲм•• мёЎм • м—ӯмӢң к°Җм •нҳҲм•• мёЎм •кіј мң мӮ¬н•ҳкІҢ мқјмғҒмғқнҷң мғҒнҷ©мқ„ л°ҳмҳҒн•ҳл©° н•ҳлЈЁ лҸҷм•Ҳ м—¬лҹ¬ лІҲмқҳ нҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқ„ м ңкіөн• мҲҳ мһҲлҠ” мһҘм җмқҙ мһҲлӢӨ. лҳҗн•ң лӢӨм–‘н•ң мһҗм„ё л°Ҹ нҷҳкІҪм—җм„ң мёЎм •мқҙ к°ҖлҠҘн•ҳл©° мқјмғҒм Ғмқё мЈјк°„ нҷңлҸҷ л°Ҹ мҲҳл©ҙ мӨ‘м—җлҸ„ нҳҲм••мқ„ мёЎм •н• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ[11]. кІҖмҰқлҗң мһҗлҸҷ нҳҲм••кі„лҘј мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳм—¬ 24мӢңк°„м—җ кұёміҗ мЈјк°„м—җлҠ” 15-30분, м•јк°„м—җлҠ” 30-60분 к°„кІ©мңјлЎң нҳҲм••мқ„ мёЎм •н•ҳл©° мҳҲмғҒ мёЎм • нҡҹмҲҳмқҳ мөңмҶҢ 70% мқҙмғҒмқҳ нҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқ„ н•ҳкІҢ лҗңлӢӨ. мқҙлҘј нҶөн•ҳм—¬ 24мӢңк°„ нҸүк· нҳҲм••мқ„ мёЎм •н• мҲҳ мһҲкі м§„лЈҢмӢӨм—җм„ңмқҳ нҳҲм•• мёЎм •мңјлЎң нҢҗлӘ…лҗҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ” м Җн•ӯм„ұ кі нҳҲм••мқ„ мӢқлі„н• мҲҳ мһҲмңјл©° 24мӢңк°„ нҳҲм•• ліҖлҸҷм„ұ л°Ҹ м•„м№Ё нҳҲм•• мҰқк°Җ, м•јк°„ нҳҲм•• ліҖлҸҷ м •лҸ„ л“ұмқҳ нҠ№м„ұмқ„ м •лҹүнҷ”н•ҳм—¬ мӢ¬нҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳмқҳ мҳҲнӣ„мҷҖ мӮ¬л§қлҘ мқ„ лҚ” мһҳ мҳҲмёЎн• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ[11,21-23]. к·ёлҹ¬лӮҳ нҷңлҸҷнҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқҖ мһҰмқҖ мӮ¬мҡ©м—җлҠ” м Ғн•©н•ҳм§Җ м•Ҡкі н•„мҡ” 비мҡ©мқҙ м Ғм§Җ м•Ҡмңјл©° мқјл°ҳ мқҳлЈҢ кё°кҙҖм—җм„ң л„җлҰ¬ мқҙмҡ©н•ҳкё°м—җ м–ҙл ӨмӣҖмқҙ мһҲкі мҲҳл©ҙ мӨ‘м—җ мқјл¶Җ нҷҳмһҗм—җкІҢ л¶ҲнҺёмқ„ мӨ„ мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨлҠ” лӢЁм җмқҙ мһҲлӢӨ[11]. мқҙмҷё мӨ‘мҡ”н•ң м ңн•ңм җмңјлЎңлҠ” мһ„мғҒ мҳҲнӣ„м—җ лҜём№ҳлҠ” мҳҒн–Ҙмқ„ нғҗмғүн•ҳкё° мң„н•ң м„ н–ү л¬ҙмһ‘мң„ лҢҖмЎ° м—°кө¬к°Җ м—Ҷм–ҙ м№ҳлЈҢмқҳ нҳҲм•• мһ„кі„м№ҳмҷҖ лӘ©н‘ңк°Җ мҲҳлҰҪлҗҳм–ҙ мһҲм§Җ лӘ»н•ң м җмқҙ мһҲлӢӨ. л°ұмқҳ нҡЁкіјк°Җ м ңкұ°лҗҳлҠ” м җмқ„ кі л Өн•ҳм—¬ нҷңлҸҷ нҳҲм••мқҖ 진лЈҢмӢӨм—җм„ң мёЎм •лҗң нҳҲм••м—җ 비н•ҙ лӮ®лӢӨкі м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲмңјл©° нҷңлҸҷнҳҲм••мңјлЎң мёЎм •лҗң 24мӢңк°„ нҸүк· мҲҳ축기нҳҲм••мқҙ 130 mmHg лҳҗлҠ” нҷ•мһҘкё°нҳҲм••мқҙ 80 mmHgк°Җ 진лЈҢмӢӨм—җм„ң мёЎм •лҗң нҳҲм•• 140 mmHg лҳҗлҠ” 90 mmHgм—җ к°Ғк°Ғ н•ҙлӢ№н•ңлӢӨ(Table 1) [24].к°Җм •нҳҲм•• мёЎм •кіј нҷңлҸҷнҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқ„ нҶөн•ҳм—¬ л°ұмқҳкі нҳҲм••кіј к°Җл©ҙкі нҳҲм••мқ„ м°ҫм•„лӮј мҲҳ мһҲлҠ” мһ„мғҒм Ғ нҠ№мһҘм җмқҙ мһҲмңјлҜҖлЎң 1лӢЁкі„ кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗ нҳ№мқҖ кі нҳҲм••м—җ к°Җк№Ңмҡҙ м •мғҒ нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗм—җкІҢм„ң к°Җм •нҳҲм•• мёЎм •кіј нҷңлҸҷнҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқ„ кі л Өн• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ[11]. лҳҗн•ң 진лЈҢмӢӨм—җм„ңмқҳ нҳҲм•• мёЎм • мӢң ліҖлҸҷмқҙ м»Өм„ң кі нҳҲм•• 진лӢЁм—җ лӘ…нҷ•н•ң кІ°м •мқ„ лӮҙлҰ¬кё° м–ҙл Өмҡҙ кІҪмҡ°, кё°лҰҪм„ұ нҳ№мқҖ мӢқнӣ„ м ҖнҳҲм••мқҙ мқҳмӢ¬лҗҳлҠ” кІҪмҡ°м—җ кі л Өн• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. 추к°Җм ҒмңјлЎң к°Җм •нҳҲм•• мёЎм •кіј нҷңлҸҷнҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқҙ кі л Өлҗҳм–ҙм•ј н•ҳлҠ” мӮ¬м•ҲмңјлЎңлҠ” нҳҲм•• ліҖлҸҷм„ұмқҳ мёЎм •мқҙ мһҲлӢӨ. нҳҲм••мқҖ н•ҳлЈЁ лҸҷм•Ҳ л§Өмҡ° ліҖлҸҷм„ұмқҙ лҶ’мңјл©° нҠ№нһҲ мЈјк°„м—җлҠ” к·ё ліҖлҸҷмқҙ нҒ°лҚ° 24мӢңк°„, мҷёлһҳ л°©л¬ё к°„ лҳҗлҠ” мһҘкё°м Ғмқё нҳҲм•• ліҖлҸҷм„ұмқҙ 24мӢңк°„ нҸүк· нҳҲм••кіј лҸ…лҰҪм ҒмңјлЎң мӢ¬нҳҲкҙҖ кІ°кіјм—җ л¶Җм •м ҒмңјлЎң м—°кҙҖлҗҳм–ҙ мһҲмқҢмқҙ 진лЈҢмӢӨм—җм„ңмқҳ нҳҲм•• мёЎм •мқ„ нҶөн•ҙ м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲлӢӨ[23,25]. мқҙм—җ 2023 мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқём—җм„ңлҠ” нҳҲм•• ліҖлҸҷм„ұ мёЎм •мқҳ мӨ‘мҡ”м„ұмқ„ к°•мЎ°н•ҳкі мһҲлӢӨ. м№ҳлЈҢ мӨ‘мқё кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗмқҳ мӢ¬нҳҲкҙҖ мң„н—ҳмқ„ ліҙлӢӨ м •нҷ•н•ҳкІҢ нҸүк°Җн•ҳлҠ” лҚ° 진лЈҢмӢӨм—җм„ңмқҳ нҳҲм•• мёЎм •лҝҗ м•„лӢҲлқј нҳҲм•• ліҖлҸҷм„ұлҸ„ кі л Өн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ мң мҡ©н•Ёмқ„ мһ„мғҒмқҳк°Җ нҢҢм•…н•ҳкі м№ҳлЈҢлҘј л°ӣлҠ” нҷҳмһҗл“Өм—җкІҢм„ң ліҖлҸҷ м—Ҷмқҙ мқјкҙҖм„ұ мһҲкІҢ нҳҲм••мқ„ мЎ°м Ҳн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ мӨ‘мҡ”н•Ёмқ„ к°•мЎ°н•ҳм—¬ көҗмңЎн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ.- 3. кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗмқҳ нҸүк°Җ
- 3. кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗмқҳ нҸүк°Җ
кі нҳҲм••мқ„ 진лӢЁн•ҳкі нҸүк°Җн•ҳкё° мң„н•ҙм„ңлҠ” мІ«м§ё, мқјм°Ём„ұкіј мқҙм°Ём„ұ кі нҳҲм••мқ„ к°җлі„н•ҳкі л‘ҳм§ё, кі нҳҲм••мқҳ мӨ‘мҰқлҸ„лҘј нҸүк°Җн•ҳл©° м…Ӣм§ё, мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳмқҳ мң„н—ҳмқёмһҗмҷҖ мғқнҷң мҠөкҙҖмқ„ нҢҢм•…н•ҳкі л§Ҳм§Җл§үмңјлЎң мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳ мң л¬ҙмҷҖ м№ҳлЈҢм—җ мҳҒн–Ҙмқ„ мӨ„ мҲҳ мһҲлҠ” лҸҷл°ҳм§Ҳнҷҳ лҳҗлҠ” л¬ҙмҰқмғҒ мһҘкё° мҶҗмғҒ мң л¬ҙлҘј нҷ•мқён•ҙм•ј н•ңлӢӨ. 2023 мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқём—җм„ңлҠ” мң„м—җ м„ңмҲ лҗң кі нҳҲм••мқҳ л“ұкёүкіј лӢЁкі„мқҳ к°ңл…җмқ„ лҸ„мһ…н•ҳкІҢ лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ.кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗм—җм„ң нҸүк°ҖлҘј мң„н•ң 진찰 л°Ҹ кІҖмӮ¬лҘј н•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҖ н–Ҙнӣ„мқҳ мң„н—ҳлҸ„м—җ м°Ёмқҙк°Җ мһҲкё° л•Ңл¬ёмқҙлӢӨ. мёЎм •лҗҳлҠ” нҳҲм••мқҳ мҲҳм№ҳм—җ л”°лқј л“ұкёү(grade)мқҖ ліҖн• мҲҳ мһҲм§Җл§Ң лӢЁкі„(stage)лҠ” мқјл°ҳм ҒмңјлЎң ліҖн•ҳкё° м–ҙл өлӢӨ. кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗлҠ” лӢӨлҘё мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳ мң„н—ҳмқёмһҗлҘј лҸҷл°ҳн•ҳлҠ” кІҪмҡ°к°Җ л§Һм•„ нҳҲм•• мЎ°м Ҳл§ҢмңјлЎң кҙҖл Ё мң„н—ҳмқ„ мЎ°м Ҳн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ 충분н•ҳм§Җ м•Ҡмңјл©° л¬ҙмҰқмғҒ нҷҳмһҗм—җм„ңлҸ„ кі нҳҲм•• м—°кҙҖ мһҘкё° мҶҗмғҒмқҙ л§Һмқҙ нҷ•мқёлҗҳкі мһҲкё° л•Ңл¬ём—җ мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖ мң„н—ҳлҸ„ мӮ°м¶ңмқ„ мң„н•ҙм„ңлҠ” л°ҳл“ңмӢң мӨ‘мҡ” м§Җн‘ң мҠӨнҒ¬лҰ¬лӢқмқ„ н•ҙм•ј н•ңлӢӨкі 2023 мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқём—җм„ң к°•мЎ°лҗҳкі мһҲлӢӨ[11]. м „м—җлҠ” н‘ңм Ғ мһҘкё° мҶҗмғҒ(end-organ damage) л“ұмқҳ н‘ңнҳ„мқ„ мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳмҳҖмңјлӮҳ мөңк·јм—җлҠ” кө¬мЎ°м Ғ/кё°лҠҘм Ғ, лҢҖнҳҲкҙҖ/мҶҢнҳҲкҙҖмқҳ к°ңл…җмқ„ лӘЁл‘җ нҸ¬н•Ён•ҳм—¬ кі нҳҲм•• м—°кҙҖ мһҘкё° мҶҗмғҒ(hypertension-mediated organ damage)мқҙлқјлҠ” н‘ңнҳ„мңјлЎң к°ңм •н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ(Fig. 1). мқҙл ҮкІҢ нҸүк°Җлҗң кі нҳҲм••мқҳ л“ұкёүкіј лӢЁкі„м—җ л”°лқј мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖ мң„н—ҳлҸ„лҘј кі„мёөнҷ”н•ҳмҳҖмңјл©° Fig. 2м—җ м ңмӢңлҗң л°”мҷҖ к°ҷмқҙ мң лҹҪмқҳ кІҪмҡ° SCORE2 нҳ№мқҖ SCORE2-OP л“ұмқҳ к°ңлі„ мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖ мң„н—ҳлҸ„ мҳҲмёЎ лҸ„кө¬к°Җ мһҲм–ҙ мқҙлҘј кё°л°ҳмңјлЎң кі„мёөнҷ” м§ҖлҸ„лҘј м ңмӢңн•ҳмҳҖкі көӯлӮҙ нҷҳмһҗлҘј лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң н•ң кі„мёөнҷ” м§ҖлҸ„лҠ” нҳ„мһ¬ к°ңл°ң мӨ‘мқҙлӢӨ[26,27]. мқҙлҹ¬н•ң мң„н—ҳлҸ„ кі„мёөнҷ” м ‘к·ј м „лһөмқҖ нҠ№нһҲ лҶ’мқҖ м •мғҒ нҳҲм•• нҳ№мқҖ 1лҸ„ кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗм—җм„ң кі нҳҲм•• м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мӢңмһ‘н• м§ҖлҘј кІ°м •н•ҳлҠ” мӨ‘мҡ”н•ң к·јкұ°к°Җ лҗңлӢӨ. кі нҳҲм•• м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ мЎ°кё°м—җ 진н–үлҗңлӢӨл©ҙ мқјл¶Җ кі нҳҲм•• м—°кҙҖ мһҘкё° мҶҗмғҒмқҙ нҡҢліөлҗ мҲҳ мһҲкё° л•Ңл¬ёмқҙлӢӨ[28]. кі нҳҲм••мқҙ мҳӨлһҳ м§ҖмҶҚлҗ кІҪмҡ° 추нӣ„ м№ҳлЈҢлҘј нҶөн•ҳм—¬ нҳҲм••мқ„ мЎ°м Ҳн•ҳлҚ”лқјлҸ„ кі нҳҲм•• м—°кҙҖ мһҘкё° мҶҗмғҒмқҙ нҡҢліөлҗҳм§Җ м•Ҡмқ„ мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ[28].- 4. кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗмқҳ м•Ҫл¬ј м№ҳлЈҢ мӢңмһ‘кіј лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм••
- 4. кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗмқҳ м•Ҫл¬ј м№ҳлЈҢ мӢңмһ‘кіј лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм••
кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗмқҳ нҸүк°Җк°Җ мӨ‘мҡ”н•ң мқҙмң лҠ” кі нҳҲм•• м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мӢңмһ‘н•ҳкі мһҗ н• л•Ңм—җлҠ” м ңлҢҖлЎң мёЎм •лҗң нҳҲм••мқҳ мҲҳм№ҳлҝҗ м•„лӢҲлқј к°ңк°ңмқёмқҳ кё°м Җ мң„н—ҳлҸ„лҘј кі л Өн•ҳм—¬м•ј н•ҳкё° л•Ңл¬ёмқҙлӢӨ. мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳмқҙ м—ҶлҠ” нҷҳмһҗмҷҖ мһҲлҠ” нҷҳмһҗмқҳ м№ҳлЈҢ мӢңмһ‘ мӢңм җмқҖ лӢӨлҘҙлӢӨ. мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳмқҳ мң„н—ҳлҸ„к°Җ лҶ’мқҖ нҷҳмһҗмқјмҲҳлЎқ к°ҷмқҖ м •лҸ„мқҳ нҳҲм••мқ„ л–Ём–ҙлңЁлҰҙ л•Ң кё°лҢҖлҗҳлҠ” мқҙл“қмқҙ лҶ’лӢӨкі м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲлӢӨ[29].кі нҳҲм•• м№ҳлЈҢлҘј нҶөн•ҳм—¬ мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳмқ„ мҳҲл°©н•ҳлҠ” нҡЁкіјк°Җ м•„л¬ҙлҰ¬ мҡ°мҲҳн•ҳм—¬лҸ„ кі нҳҲм•• м „ лӢЁкі„м—җм„ң м•Ҫл¬ј м№ҳлЈҢлҠ” к¶Ңкі н•ҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ”лӢӨ. нҳҲм••м—җ л”°лҘё мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳмқҳ мӮ¬л§қлҘ мқҖ 115/75 mmHgм—җм„ң мҲҳ축기нҳҲм••мқҙ 20 mmHg, нҷ•мһҘкё°нҳҲм••мқҙ 10 mmHgм”© мҰқк°Җн•Ём—җ л”°лқј 2л°°м”© кі„мҶҚ мҰқк°Җн•ңлӢӨ[29]. мҰү нҳҲм••мқҙ 120/80 mmHg мқҙмғҒмқё кІҪмҡ°м—җлҠ” кі нҳҲм••мқҳ л°ңмғқ л°Ҹ мӢ¬нҳҲкҙҖ мӮ¬кұҙмқ„ мҳҲл°©н•ҳкё° мң„н•ҳм—¬ м Ғк·№м Ғмқё мғқнҷң мҡ”лІ•мқ„ к¶Ңкі н•ҳм—¬м•ј н•ңлӢӨ[30,31]. м•„м§Ғ кі нҳҲм•• м „ лӢЁкі„м—җм„ң мЎ°кё° м•Ҫл¬ј м№ҳлЈҢмқҳ нҡЁкіјлҠ” лӘ…нҷ•н•ҳм§Җ м•ҠлӢӨ[31]. лӢӨл§Ң лҶ’мқҖ м •мғҒ нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗ мӨ‘ кі нҳҲм••мқҳ лӢЁкі„к°Җ лҶ’м•„ кі мң„н—ҳ нҳ№мқҖ мөңкі мң„н—ҳ к·ёлЈ№мңјлЎң нҸүк°ҖлҗҳлҠ” кІҪмҡ° м№ҳлЈҢ нҡЁкіјк°Җ мһҲлӢӨ[32]. мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖ мң„н—ҳлҸ„к°Җ м Җмң„н—ҳкө°мқё 1лҸ„ кі нҳҲм••мқё кІҪмҡ° м•Ҫл¬ј м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мӢңмһ‘н•ҳлҠ” кІғм—җ лҢҖн•ң мһ„мғҒ к·јкұ°к°Җ лӢӨмҶҢ л№Ҳм•Ҫн•ҳм—¬ мғқнҷң мҡ”лІ•мқ„ лЁјм Җ мӢңн–үн•ң нӣ„ мЎ°м Ҳлҗҳм§Җ м•Ҡмқ„ л•Ң м•Ҫл¬ј м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мӢңмһ‘н•ҳлҸ„лЎқ к¶Ңкі лҗҳл©° мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖ мң„н—ҳлҸ„к°Җ мһҲлҠ” 1лҸ„ кі нҳҲм•• нҳ№мқҖ кі нҳҲм••мқҳ л“ұкёүмқҙ 2лҸ„ кі нҳҲм•• мқҙмғҒмқј кІҪмҡ° л°”лЎң м•Ҫл¬ј м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мӢңмһ‘н•ҳлҸ„лЎқ к¶Ңкі лҗңлӢӨ[29,33]. лӢӨл§Ң 80м„ё мқҙмғҒмқҳ кі л № нҷҳмһҗмқҳ кІҪмҡ° мҲҳ축기нҳҲм••мқҙ 160 mmHg мқҙмғҒмқј мӢң кі нҳҲм•• м№ҳлЈҢлҘј кі л Өн• мҲҳ мһҲмңјл©° мқҙлҹ¬н•ң кІ°м •мқҖ нҷҳмһҗ к°ңмқёмқҳ мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖ мң„н—ҳлҸ„ л°Ҹ мң„м•Ҫмқҳ м •лҸ„лҘј к°җм•Ҳн•ҳм—¬ к°ңлі„м ҒмңјлЎң м ‘к·јн•ҙм•ј н•ңлӢӨкі к¶Ңкі лҗҳкі мһҲлӢӨ.мқјм°Ём ҒмңјлЎң нҳҲм••мқ„ лӮ®м¶”кё° мң„н•ң лӘ©м ҒмңјлЎң н•ӯкі нҳҲм••м•Ҫмқ„ ліөмҡ©н•ң нҷҳмһҗм—җм„ң лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм••м—җ кҙҖн•ң м—°кө¬лЎң strategy of blood pressure intervention in the elderly hypertensive patients (STEP) л°Ҹ action to control cardiovascular risk in diabetes (ACCORD) м—°кө¬к°Җ мһҲмңјлӮҳ мөңк·јмқҳ л©”нғҖ 분м„қм—җм„ңлҠ” мӢ¬нҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳмқҙ м—ҶлҠ” кі мң„н—ҳкө° нҷҳмһҗлҘј 140/90 mmHg мқҙмғҒмқҳ нҳҲм••м—җм„ң м•Ҫл¬ј м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мӢңмһ‘н•ҳм—¬ мҲҳ축기нҳҲм••мқ„ 130 mmHg к°Җк№Ңмқҙ лӮ®м¶”лҠ” кІғмқҙ мӢ¬нҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳм—җ лҢҖн•ң мҳҲл°© нҡЁкіјк°Җ к°ҖмһҘ лӣ°м–ҙлӮ¬кё° л•Ңл¬ём—җ мӢ¬нҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳмқҙ м—ҶлҠ” кі мң„н—ҳкө°м—җ лҢҖн•ҳм—¬ нҳҲм••мқ„ 130/80 mmHgк№Ңм§Җ лӮ®м¶”лҸ„лЎқ к¶Ңкі н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ[34]. лӢӨл§Ң 2023 мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқём—җлҠ” лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм••мқҳ мғҒн•ңм„ лҝҗл§Ң м•„лӢҲлқј н•ҳн•ңм„ мқ„ м ңмӢңн•ҳм—¬ кі нҳҲм•• м№ҳлЈҢ мӢң л¬ҙмЎ°кұҙм ҒмңјлЎң нҳҲм••мқ„ лӮ®м¶”лҠ” кІғмқҙ м•„лӢҳмқ„ к°•мЎ°н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ(Fig. 3). лҳҗн•ң м—°л №мқ„ лӮҳлҲ„м–ҙ м„ёл¶Җ лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм••мқ„ м ңмӢңн•ҳмҳҖлҠ”лҚ° 18-64м„ёмқҳ кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗлҠ” лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм••мқ„ 130/80 mmHg лҜёл§ҢмңјлЎң м ңмӢңн•ҳм—¬ м Ғк·№м Ғ к°•м••мқ„ м ңмӢңн•ҳмҳҖкі 65-79м„ёмқҳ кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗлҠ” лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм••мқ„ 140/80 mmHg лҜёл§Ң, 65-79м„ёмқҳ мҲҳ축기 лӢЁлҸ… кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗлҠ” мҲҳ축기нҳҲм•• 140-150 mmHg, 80м„ё мқҙмғҒмқҳ кі л № нҷҳмһҗмқҳ кІҪмҡ° лӘ©н‘ң мҲҳ축기нҳҲм••мқҙ 140-150 mmHgмқҙлӮҳ нҷҳмһҗк°Җ л¶Җмһ‘мҡ©мқҙ м—Ҷмңјл©ҙ 130-139 mmHgк№Ңм§Җ мЎ°м Ҳмқҙ к°ҖлҠҘн•ҳлӢӨ. лӢӨл§Ң мҲҳ축기нҳҲм••мқҙ 70 mmHg мқҙн•ҳлЎң м Җн•ҳлҗҳлҠ” мғҒнҷ©мқҖ мЈјмқҳн•ҳм—¬м•ј н•ңлӢӨлҠ” 세분нҷ”лҗң к¶Ңкі к°Җ мӢӨл ӨмһҲлӢӨ[35-37].- 5. кі нҳҲм••мқҳ м•Ҫл¬ј м№ҳлЈҢ
- 5. кі нҳҲм••мқҳ м•Ҫл¬ј м№ҳлЈҢ
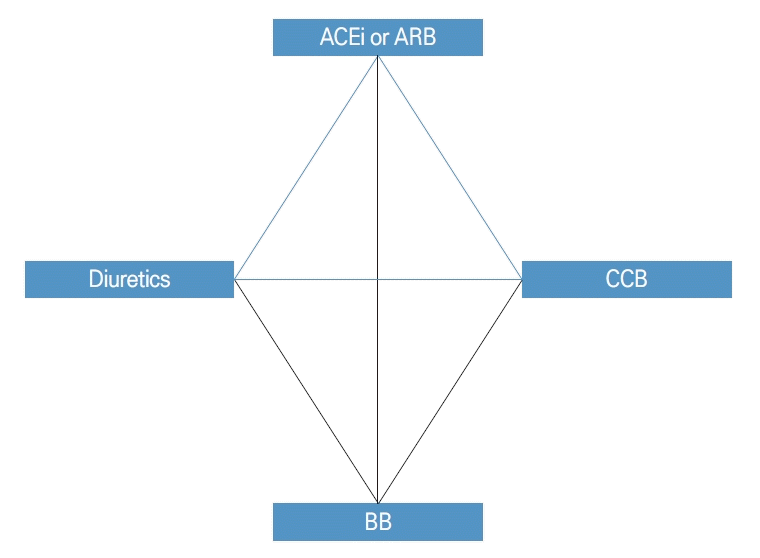
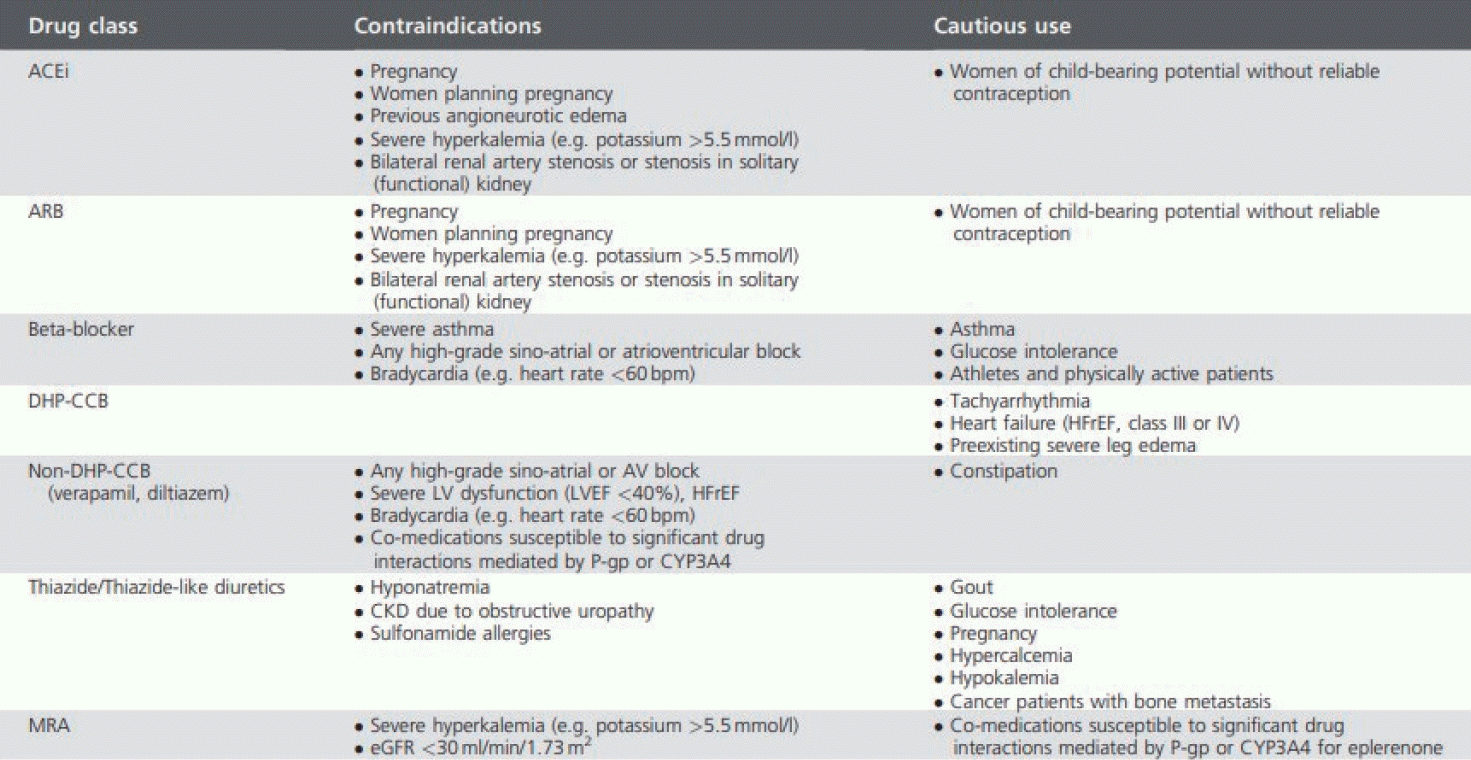
2023 мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқём—җм„ңлҸ„ мқҙм „ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқёкіј к°ҷмқҙ кё°мЎҙм—җ к°ҖмһҘ л§Һмқҙ мӮ¬мҡ©лҗҳлҠ” 5лҢҖ кі„м—ҙ м•Ҫм ңм—җ лҢҖн•ң мҶҢк°ңлҠ” мң м§Җлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ[38]. 5лҢҖ кі„м—ҙ м•Ҫм ңлҠ” м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ м „нҷҳнҡЁмҶҢм–өм ңм ң(angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors), м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ IIмҲҳмҡ©мІҙм°ЁлӢЁм ң(angiotension II receptor blockers), м№јмҠҳнҶөлЎңм°ЁлӢЁм ң(calcium channel blockers), мӢёмқҙм•„мһҗмқҙл“ң лҳҗлҠ” мӢёмқҙм•„мһҗмқҙл“ң мң мӮ¬мқҙлҮЁм ң(thiazide/thiazide-like diuretics), лІ нғҖм°ЁлӢЁм ң(beta blockers)мқҙлӢӨ. кё°мЎҙ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқёкіј лӢӨлҘё м°Ёмқҙм җмқҖ лІ нғҖм°ЁлӢЁм ңмқҳ мӨ‘мҡ”м„ұмқҙ л¶Җк°Ғлҗң м җкіј SGLT2м–өм ңм ң(sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 [SGLT2] inhibitors) л°Ҹ 비мҠӨн…ҢлЎңмқҙл“ңл¬ҙкё°м§ҲмҪ”лҘҙнӢ°мҪ”мқҙл“ңкёён•ӯм ң(nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists) л“ұмқҳ м•Ҫм ңк°Җ мӮ¬мҡ© к°ҖлҠҘн•ҳкі нҡЁкіјм Ғмқё кі„м—ҙлЎң 추к°Җлҗң м җмқҙ мһҲлӢӨ.л№ лҘё нҡЁкіјлҘј мң„н•ҳм—¬ мқјм°Ё м№ҳлЈҢ м•Ҫм ңлЎң кі л №, лҶ’мқҖ м •мғҒ нҳҲм••, 1лҸ„мқҳ м Җмң„н—ҳ кі нҳҲм•• нҷҳмһҗ мҷёмқҳ лҢҖл¶Җ분мқҳ нҷҳмһҗм—җм„ң 2м ң лі‘мҡ© мҡ”лІ•мқ„ мӢңмһ‘н• кІғмқҙ к¶Ңкі лҗҳкі мһҲмңјл©° 2м ң мҡ”лІ• мӢң м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ м „нҷҳнҡЁмҶҢм–өм ңм ң/м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ IIмҲҳмҡ©мІҙм°ЁлӢЁм ң кі„м—ҙм—җ лҚ”н•ҳм—¬ мӢёмқҙм•„мһҗмқҙл“ң лҳҗлҠ” мӢёмқҙм•„мһҗмқҙл“ң мң мӮ¬мқҙлҮЁм ң кі„м—ҙ нҳ№мқҖ м№јмҠҳнҶөлЎңм°ЁлӢЁм ң кі„м—ҙмқ„ мқҙмҡ©н• кІғмқ„ 추мІңн•ҳкі мһҲлӢӨ. 3м ң мҡ”лІ•мқҳ кІҪмҡ° мң„м—җ м–ёкёүн•ң 3к°ң кі„м—ҙмқҳ м•Ҫм ңлҘј мӢңмһ‘н•ҙ ліј мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ(Fig. 4). м•Ҫм ңлҘј мӮ¬мҡ©н• мӢңм—җлҠ” к°Ғ кі„м—ҙлі„ мң мқҳм җмқ„ мӮ¬м „м—җ мҲҷм§Җн•ҳм—¬м•ј н•ңлӢӨ(Fig. 5).мқҙм „мқҳ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқём—җм„ңлҠ” лӢӨлҘё кі„м—ҙмқҳ нҳҲм•• мЎ°м Ҳ м•Ҫм ңл“Өкіј 비көҗ мӢң лІ нғҖм°ЁлӢЁм ңк°Җ лҮҢмЎёмӨ‘м—җ лҢҖн•ң мң„н—ҳлҸ„ к°җмҶҢ нҡЁкіјк°Җ м ҒмқҖ м җкіј лҢҖмӮ¬мҰқнӣ„кө° нҷҳмһҗм—җм„ң мӢ к·ң л°ңмғқ лӢ№лҮЁлі‘ л№ҲлҸ„к°Җ лҶ’м•ҳлҚҳ м җмқҙ м•Ҫм җмқҙм—ҲмңјлӮҳ 2023 мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқём—җм„ңлҠ” кёүм„ұ/л§Ңм„ұ кҙҖмғҒлҸҷл§Ҙм§Ҳнҷҳ, мӢ¬к·јкІҪмғү нӣ„ л¶Җм •л§Ҙ, нҳ‘мӢ¬мҰқ, мӢ¬л¶Җм „, мӢ¬л°©м„ёлҸҷ, мһ„мӮ°л¶Җ л°Ҹ мһ„мӢ кі„нҡҚ мӢң л“ұ нҠ№м • мһ„мғҒ мғҒнҷ©м—җм„ң лІ нғҖм°ЁлӢЁм ңк°Җ мң лҰ¬н•ң нҡЁкіјк°Җ мһҲлҠ” м җмқҙ м ңмӢңлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ[39-41]. лӢӨл§Ң мқҙлҹ¬н•ң мқҙм җмқҙ мһҲмқҢм—җлҸ„ мІңмӢқ, л§Ңм„ұ нҸҗмҮ„м„ұ нҸҗм§Ҳнҷҳ, 2-3лҸ„ л°©мӢӨм „лҸ„мһҘм• , лҢҖмӮ¬мҰқнӣ„кө° нҷҳмһҗ л°Ҹ л…ёмқё нҷҳмһҗм—җкІҢ нҲ¬м—¬ мӢң мЈјмқҳн•ҳм—¬м•ј н•ңлӢӨ.нҳ„мһ¬ н•ӯкі нҳҲм•• м•Ҫл¬ј м№ҳлЈҢмқҳ 주축мқ„ лӢҙлӢ№н•ҳлҠ” кі„м—ҙмқҖ м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ м „нҷҳнҡЁмҶҢм–өм ңм ң, м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ IIмҲҳмҡ©мІҙм°ЁлӢЁм ңлЎң нҳҲм•• к°•н•ҳ мқҙмҷём—җлҸ„ мӢ¬нҳҲкҙҖ л°Ҹ кі нҳҲм•• м—°кҙҖ м§Ҳнҷҳмқё мӢ¬к·јкІҪмғүмҰқ, мӢ¬л¶Җм „, кҙҖмғҒлҸҷл§Ҙм§Ҳнҷҳ, лӢ№лҮЁлі‘м„ұ мӢ мҰқ л°Ҹ л§Ңм„ұ мҪ©нҢҘлі‘ л“ұм—җм„ң мҡ°мҲҳн•ң нҡЁкіјк°Җ мҰқлӘ…лҗҳм–ҙ нҳ„мһ¬ нҠ№лі„н•ң кёҲкё°к°Җ м—ҶлҠ” н•ң кі нҳҲм•• 1м°Ё м•Ҫм ңлЎң л„җлҰ¬ мӮ¬мҡ©лҗҳкі мһҲлӢӨ[42,43]. мӢ мһҘ ліҙнҳё нҡЁкіјм—җлҸ„ л¶Ҳкө¬н•ҳкі м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ м „нҷҳнҡЁмҶҢм–өм ңм ң, м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ IIмҲҳмҡ©мІҙм°ЁлӢЁм ңлҠ” мҪ©нҢҘ кё°лҠҘмқ„ м•Ҫнҷ”мӢңмјңм„ң нҳҲмІӯ нҒ¬л Ҳм•„нӢ°лӢҢмқҙ мғҒмҠ№н• мҲҳ мһҲмңјлҜҖлЎң нҲ¬м•Ҫ мӢң мІҳмқҢ 1-2к°ңмӣ” лӮҙм—җ нҳҲм•Ў кІҖмӮ¬лҘј мӢңн–үн•ҳм—¬ нҒ¬л Ҳм•„нӢ°лӢҢмқҙ 30% мқҙмғҒ мғҒмҠ№н•ҳкұ°лӮҳ нҳҲмӨ‘ м№јлҘЁмқҙ 5.5 mEq/L мқҙмғҒ мҰқк°Җн•ҳлҠ”м§Җм—җ лҢҖн•ң лӘЁлӢҲн„°л§Ғмқҙ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ. нҠ№нһҲ л§Ңм„ұ мҪ©нҢҘлі‘ нҷҳмһҗлЎң нҳҲмІӯ нҒ¬л Ҳм•„нӢ°лӢҢмқҙ 3.0 mg/dL мқҙмғҒмқё кІҪмҡ° кі м№јлҘЁнҳҲмҰқмқҳ л°ңмғқм—җ мЈјмқҳн•ҙм•ј н•ңлӢӨ. м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ м „нҷҳнҡЁмҶҢм–өм ңм ң, м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ IIмҲҳмҡ©мІҙм°ЁлӢЁм ңлҠ” нғңм•„м—җ кё°нҳ•мқ„ мҙҲлһҳн•ҳлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲм–ҙм„ң мһ„мӢ л¶Җм—җкІҢлҠ” кёҲкё°мқҙл©° мһ„мӢ мқҙ мҳҲм •лҗҳм–ҙ мһҲкұ°лӮҳ к°Җмһ„л¶Җм—җм„ңлҠ” нҲ¬м•Ҫ мӢң мЈјмқҳн•ҙм•ј н•ңлӢӨ.л ҲлӢҢ-м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ -м•ҢлҸ„мҠӨн…ҢлЎ кі„(renin angiotensin aldosterone system)мқҳ л§Ҳм§Җл§ү лӢЁкі„м—җм„ң мһ‘мҡ©н•ҳлҠ” 비мҠӨн…ҢлЎңмқҙл“ңл¬ҙкё°м§ҲмҪ”лҘҙнӢ°мҪ”мқҙл“ңкёён•ӯм ң(nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists)мқё мҠӨн”јлЎңлҶҖлқҪнҶӨ(spironolactone) л°Ҹ м—җн”Ңл Ҳл Ҳл…ј(eplerenone)мқҳ кІҪмҡ° мӢ¬л°•м¶ңлҹүк°җмҶҢ мӢ¬л¶Җм „(heart failure with reduced ejection fraction)м—җм„ң мӮ¬мҡ©лҗҳлӮҳ нҳҲм•• к°•н•ҳ нҡЁкіјмқҳ к°ҖлҠҘм„ұ м—ӯмӢң м ңмӢңлҗҳм–ҙ мһҲлӢӨ[44]. лҳҗн•ң м—ӯмӢң м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ кі„м—җ кҙҖм—¬н•ҳлҠ” м•Ҫм ңлЎң м•Ҳм§ҖмҳӨн…җмӢ мҲҳмҡ©мІҙ м–өм ңм ңмҷҖ лӮҳнҠёлҘЁмқҙлҮЁнҺ©нғҖмқҙл“ңлҘј 분н•ҙн•ҳлҠ” л„Өн”„лҰҙлҰ¬мӢ мқ„ м–өм ңн•ҳлҠ” м•Ҫм ңмқҳ лі‘мҡ© мҡ”лІ•(angiotension receptor-neprylisin inhibitor, valsartan-sacubitril)мқҙ мҶҢк°ңлҗҳм–ҙ мһҲлӢӨ. мӢ¬л¶Җм „ нҷҳмһҗм—җм„ң мҠ№мқёлҗң м•Ҫм ңмқҙлӮҳ мөңк·ј л©”нғҖ м—°кө¬м—җм„ң кё°нғҖ кі„м—ҙмқҳ кі нҳҲм•• м•Ҫм ңм—җ 비н•ҙ мҡ°мӣ”н•ң нҳҲм••мқҳ м Җн•ҳ нҡЁкіјлҘј мһ…мҰқн•ң м—°кө¬ кІ°кіјк°Җ м ңмӢңлҗҳм–ҙ мһҲм–ҙ мғҲлЎңмҡҙ нҳҲм••м•Ҫ кі„м—ҙлЎң м ңмӢңлҗҳкі мһҲлӢӨ[45].м№јмҠҳнҶөлЎңм°ЁлӢЁм ңлҠ” м Җл ҙн•ң м•Ҫк°Җ, м•Ҳм •м Ғмқё м•ҪлҸҷн•ҷм Ғ м„ұм§Ҳкіј мҡ°мҲҳн•ң мһ„мғҒ кІ°кіјлҘј кі л Өн•ҳм—¬ нҳ„мһ¬к№Ңм§Җ л„җлҰ¬ мӮ¬мҡ©лҗҳкі мһҲлӢӨ. Dihydropyridine кі„м—ҙмқҳ м№јмҠҳнҶөлЎңм°ЁлӢЁм ңмқё м•”лЎңл””н•Җ(amlodipine)мқҖ мӢ¬л°•м¶ңлҹүк°җмҶҢмӢ¬л¶Җм „ нҷҳмһҗ л“ұм—җм„ң мӮ¬мҡ©н• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. Nondihydropyridine кі„м—ҙмқҳ м№јмҠҳнҶөлЎңм°ЁлӢЁм ңмқё л”ңнӢ°м•„м ¬(diltiazem), лІ лқјнҢҢл°Җ(verapamil)мқҖ нҳҲкҙҖ 비нҠ№мқҙм Ғмқё нҠ№м„ұмқҙ мһҲмңјлӮҳ нҳҲм•• к°•н•ҳ нҡЁкіјлҘј лӮҳнғҖлӮҙл©° н•ӯл¶Җм •л§Ҙ м•Ҫм ңлЎңм„ңмқҳ нҡЁлҠҘмқҙ лҸҷл°ҳлҗҳм–ҙ мӢ¬л°©м„ёлҸҷ нҷҳмһҗм—җм„ң мӢ¬л°•мҲҳ мЎ°м Ҳмқ„ мң„н•ҙм„ң мӮ¬мҡ©н• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ[2]. м№јмҠҳнҶөлЎңм°ЁлӢЁм ңлҠ” нҳҲм•• к°•н•ҳ мқҙнӣ„м—җ л°ҳмӮ¬м Ғмқё көҗк°җмӢ кІҪ нҷңм„ұнҷ”лӮҳ л№Ҳл§Ҙ, нҳҲкҙҖ нҷ•мһҘм—җ л”°лҘё лӢӨлҰ¬ л¶Җмў…мқҙ мһҲмқ„ мҲҳ мһҲмңјлҜҖлЎң мқҙлҘј мһҳ лӘЁлӢҲн„°л§Ғн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ.мқҙлҮЁм ңмқҳ кІҪмҡ° мӢёмқҙм•„мһҗмқҙл“ңнҳ• мқҙлҮЁм ңмқё н•ҳмқҙл“ңлЎңнҒҙлЎңлЎңмӢёмқҙм•„мһҗмқҙл“ң(hydrochlorothiazide)мҷҖ мӢёмқҙм•„мһҗмқҙл“ң мң мӮ¬ мқҙлҮЁм ңмқё нҒҙлЎңлҘҙнғҲлҰ¬лҸҲ(chlorthalidone), мқёлӢӨнҢҢлҜёл“ң(indapamide)к°Җ мӮ¬мҡ©лҗҳкі мһҲлӢӨ. нҳҲм•• к°•н•ҳ мёЎл©ҙм—җм„ңлҠ” мӢёмқҙм•„мһҗмқҙл“ң мң мӮ¬мқҙлҮЁм ңк°Җ hydrochlorothiazideліҙлӢӨ нҡЁкіјк°Җ нҒ° кІғмңјлЎң л°қнҳҖ진 м—°кө¬л“Өмқҙ мһҲмңјлӮҳ мӢ¬нҳҲкҙҖкі„ мӮ¬кұҙ мҳҲл°© нҡЁкіјм—җм„ңлҠ” hydrochlorothiazideмҷҖ chlorthalidoneмқҳ мӮ¬мҡ©мқҙ мҳҲнӣ„м—җ м°Ёмқҙк°Җ лӮҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң нҷ•мқёлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ[46-48]. лӢӨл§Ң мӮ¬кө¬мІҙм—¬кіјмңЁмқҙ 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 лҜёл§Ңмқё кІҪмҡ° hydrochlorothiazideмқҳ нҡЁкіјк°Җ л–Ём–ҙм§ҖлҜҖлЎң мқҙлҹ¬н•ң кІҪмҡ°м—җлҠ” кі лҰ¬мқҙлҮЁм ңк°Җ 추мІңлҗҳл©° к·ёлҹјм—җлҸ„ мЎ°м Ҳмқҙ лҗҳм§Җ м•ҠлҠ” кІҪмҡ° chlorthalidoneмқ„ 추к°Җн• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨ. мқҙлҮЁм ңлҠ” м Җм№јлҘЁнҳҲмҰқ, м ҖлӮҳнҠёлҘЁнҳҲмҰқ, кі мҡ”мӮ°мҰқ, нҳҲлӢ№ мҰқк°Җ, кі м§ҖнҳҲмҰқ, м Җл§Ҳк·ёл„ӨмҠҳнҳҲмҰқ, кі м№јмҠҳнҳҲмҰқ л“ұ лӢӨм–‘н•ң лҢҖмӮ¬м„ұ л¶Җмһ‘мҡ©мқ„ мң л°ңн• мҲҳ мһҲм–ҙ мЈјмқҳк°Җ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ.- 6. мӢ кІҪкі„м§Ҳнҷҳм—җм„ңмқҳ кі нҳҲм•• кҙҖлҰ¬
- 6. мӢ кІҪкі„м§Ҳнҷҳм—җм„ңмқҳ кі нҳҲм•• кҙҖлҰ¬
1) лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳкіј кі нҳҲм••
1) лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳкіј кі нҳҲм••
н—ҲнҳҲ л°Ҹ м¶ңнҳҲлҮҢмЎёмӨ‘ лӘЁл‘җ нҳҲм••мқҙ лҶ’мқ„мҲҳлЎқ мң„н—ҳлҸ„к°Җ мҰқк°Җн•ҳл©° кі нҳҲм••мқҖ мЎ°м Ҳ к°ҖлҠҘн•ң лҮҢмЎёмӨ‘ мң„н—ҳмқёмһҗ мӨ‘м—җм„ң мқёкө¬ 집лӢЁм—җ лҢҖн•ң кё°м—¬ мң„н—ҳлҸ„к°Җ к°ҖмһҘ лҶ’лӢӨлҠ” м җм—җм„ң мӨ‘мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ[49,50]. кёүм„ұкё° м№ҳлЈҢмқҳ кҙҖм җм—җм„ң ліҙмһҗл©ҙ нҳҲмў… нҷ•мһҘ, нҳҲмў… мЈјмң„мқҳ л¶Җмў…, мһ¬м¶ңнҳҲкіј лҮҢм¶ңнҳҲ кёүм„ұкё°мқҳ нҳҲм•• мғҒмҠ№мқҙ м—°кҙҖлҗҳм–ҙ мһҲкё° л•Ңл¬ём—җ лҮҢм¶ңнҳҲ л°ңлі‘ нӣ„ 6мӢңк°„ мқҙлӮҙмқҳ нҷҳмһҗл“Өм—җкІҢ нҳҲм••мқ„ 140/90 mmHg лҜёл§ҢмңјлЎң лӮ®м¶”лҠ” кІғмқҙ мӢ кІҪкі„ мҳҲнӣ„лҘј к°ңм„ н• мҲҳ мһҲлӢӨкі мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқёмқҖ к¶Ңкі н•ҳкі мһҲлӢӨ[51,52]. лӢӨл§Ң лҜёкөӯмқҳ лҮҢм¶ңнҳҲ м№ҳлЈҢм§Җм№Ём—җм„ңлҠ” мқҳн•ҷм Ғ л°Ҹ мӢ кІҪн•ҷм ҒмңјлЎң м•Ҳм •лҗң нҷҳмһҗмқҳ кІҪмҡ° лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм••мқ„ 130/80 mmHg лҜёл§ҢмңјлЎң м„Өм •н•ҳлҠ” кІғмқ„ к¶Ңкі н•ҳкі мһҲлӢӨ[53,54]. кіјлҸ„н•ң нҳҲм•• к°җмҶҢ нҡЁкіјм—җ лҢҖн•ҙм„ңлҠ” нҳҲмў… мЈјмң„мқҳ лҮҢн—ҲнҳҲмқ„ мң л°ңн• мҲҳ мһҲм–ҙ мЈјмқҳк°Җ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ. кёүм„ұкё° лҮҢм¶ңнҳҲм—җм„ң нҳҲм•• к°җмҶҢмқҳ нҡЁкіјлҘј нҷ•мқён•ҳкё° мң„н•ң лҢҖн‘ңм Ғмқё л‘җ мһ„мғҒмӢңн—ҳмқё INTERACT-2мҷҖ ATACH-IIм—җ м°ём—¬н•ң нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ л©”нғҖ 분м„қ м—°кө¬м—җм„ң мҲҳ축기нҳҲм••мқҙ 60 mmHg мқҙмғҒ к°җмҶҢлҗң кІҪмҡ°м—җлҠ” лҚ” л¶Ҳлҹүн•ң мҳҲнӣ„лҘј ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ[55]. лҮҢм¶ңнҳҲ л°ңлі‘ нӣ„ 6мӢңк°„ мқҙнӣ„м—җ м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мӢңмһ‘н•ҳлҠ” нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ кІҪмҡ° л©”нғҖ 분м„қ м—°кө¬м—җм„ң нҳҲмў…мқҳ нҷ•мһҘмқҖ мӨ„мҳҖмңјлӮҳ мһ„мғҒ мҳҲнӣ„мқҳ нҡҢліөм—җлҠ” мң мқҳн•ң нҡЁкіјк°Җ м—Ҷм—ҲлӢӨ[56]. лӢӨл§Ң мҙҲкё° мҲҳ축기нҳҲм••мқҙ 220 mmHg мқҙмғҒмқј кІҪмҡ° 140-180 mmHg м•„лһҳлЎң мҲҳ мӢңк°„м—җ кұёміҗ мІңмІңнһҲ мЎ°м Ҳн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ 추мІңлҗңлӢӨ[57,58].кёүм„ұкё° н—ҲнҳҲлҮҢмЎёмӨ‘мқҳ кІҪмҡ° лҢҖл¶Җ분мқҳ нҷҳмһҗл“Өм—җм„ң мҙҲкё° нҳҲм•• мҲҳм№ҳк°Җ лҶ’мңјл©° л°ңлі‘ нӣ„ 48-72мӢңк°„ лҸҷм•Ҳ мһҗм—°м ҒмңјлЎң м җ진м Ғ к°җмҶҢлҘј ліҙмқёлӢӨ[59]. н—ҲнҳҲлҮҢмЎёмӨ‘ нӣ„ 72мӢңк°„ лҸҷм•Ҳ нҳҲм••мқҙ 220/120 mmHg мқҙн•ҳмқё кІҪмҡ° нҳҲм•• к°җмҶҢмқҳ нҡЁкіјк°Җ мқјкҙҖм„ұ мһҲкІҢ ліҙкі лҗҳм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳкё° л•Ңл¬ём—җ нҳҲм•• к°җмҶҢ м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мһҗм ңн•ҳм—¬м•ј н•ңлӢӨ. лӢӨл§Ң нҳҲм „мҡ©н•ҙм ң нҲ¬м—¬лӮҳ нҳҲм „м ңкұ°мҲ мҷҖ к°ҷмқҖ мһ¬кҙҖлҘҳ мӢңмҲ мқ„ л°ӣкұ°лӮҳ л°ӣмқ„ нҷҳмһҗл“ӨмқҖ нҳҲм••мқҙ нҳ„м Җн•ҳкІҢ лҶ’мқ„ кІҪмҡ° лҮҢм¶ңнҳҲ мң„н—ҳмқҙ мҰқк°Җн•ңлӢӨлҠ” кҙҖмёЎм Ғ м—°кө¬ кІ°кіјк°Җ мһҲмңјлҜҖлЎң мқҙлҹ¬н•ң нҷҳмһҗл“Өм—җм„ңлҠ” мҙҲкё° нҳҲм•• мЎ°м Ҳмқҙ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ. нҳҲм „мҡ©н•ҙм ң нҲ¬м—¬ нҷҳмһҗмқҳ кІҪмҡ° нҲ¬м—¬ м „ нҳҲм••мқ„ л©ҙл°ҖнһҲ лӘЁлӢҲн„°л§Ғн•ҳкі кҙҖлҰ¬н•ҳм—¬ лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм••мқё <180/110 mmHg мқҙн•ҳлЎң мң м§Җн•ҳм—¬м•ј н•ҳл©° л§Ңм•Ҫ нҷҳмһҗмқҳ нҳҲм••мқҙ мқҙліҙлӢӨ лҶ’лӢӨл©ҙ н•ӯкі нҳҲм•• м•Ҫл¬јмқ„ мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳм—¬ лӘ©н‘ң лІ”мң„лЎң нҳҲм••мқ„ лӮ®м¶ҳ нӣ„ нҳҲм „мҡ©н•ҙм ңлҘј нҲ¬м—¬н•ҳм—¬м•ј н•ңлӢӨ[60]. нҲ¬м•Ҫ мқҙнӣ„ нҳҲм••мқ„ мөңмҶҢн•ң мӢңмҲ нӣ„ мІ« 24мӢңк°„ лҸҷм•Ҳ 180/105 mmHg мқҙн•ҳлЎң мң м§Җн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ к¶Ңкі лҗҳл©° 집мӨ‘м№ҳлЈҢмӢӨ лҳҗлҠ” лҮҢмЎёмӨ‘м „л¬ёлі‘лҸҷм—җм„ң м§ҖмҶҚм ҒмңјлЎң нҳҲм••мқ„ лӘЁлӢҲн„°л§Ғн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ[60]. нҳҲм „м ңкұ°мҲ кіј к°ҷмқҖ мһ¬кҙҖлҘҳ мӢңмҲ мқ„ л°ӣмқҖ нҷҳмһҗмқҳ кІҪмҡ° нҠ№нһҲ м„ұкіөм Ғмқё мһ¬кҙҖлҘҳк°Җ лӢ¬м„ұлҗң кІҪмҡ° мөңмҶҢн•ң мӢңмҲ нӣ„ мІ« 24мӢңк°„ лҸҷм•Ҳ нҳҲм••мқ„ 180/105 mmHg мқҙн•ҳлЎң мң м§Җн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ к¶Ңкі лҗңлӢӨ[60]. нҳҲм „м ңкұ°мҲ кіј к°ҷмқҖ мһ¬кҙҖлҘҳ мӢңмҲ мқ„ л°ӣм§Җ м•ҠмқҖ нҷҳмһҗл“Өм—җм„ңлҠ” кёүм„ұ н—ҲнҳҲлҮҢмЎёмӨ‘ нӣ„ 3мқј мқҙмғҒ кі нҳҲм••мқҙ мң м§ҖлҗҳлҠ” кІҪмҡ° нҳҲм•• к°җмҶҢ м•Ҫл¬јмқ„ мІҳл°©н•ҳкұ°лӮҳ мһ¬мӢңмһ‘н•ҳлҠ” л°©м•Ҳмқҙ к¶Ңкі лҗңлӢӨ[61-63].кёүм„ұкё° мқҙнӣ„ лҮҢмЎёмӨ‘ мһ¬л°ңмқ„ мҳҲл°©н•ҳкё° мң„н•ң мөңм Ғмқҳ нҳҲм•• лӘ©н‘ңлҠ” м—¬лҹ¬ мһ„мғҒмӢңн—ҳ л°Ҹ л©”нғҖ 분м„қ м—°кө¬ кІ°кіјлҘј нҶөн•ҙ мҲҳ축기нҳҲм•• 120-140 mmHgмқҳ лІ”мң„лЎң к¶Ңкі лҗңлӢӨ[64,65]. м„ н–ү м—°кө¬м—җм„ң мҲҳ축기нҳҲм•• 120 mmHg лҜёл§Ңмқё кІҪмҡ° мҳӨнһҲл Ө лҮҢмЎёмӨ‘мңјлЎң мқён•ң мӮ¬л§қлҘ мқҙ мҰқк°Җн•ҳлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲм–ҙ мқҙм—җ лҢҖн•ң мЈјмқҳк°Җ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ[66]. мқҙлҹ¬н•ң кІ°кіјм—җлҸ„ л¶Ҳкө¬н•ҳкі нҷҳмһҗмқҳ кё°лҠҘм Ғ мғҒнғң, м·Ём•Ҫм„ұ, мқём§Җкё°лҠҘ л°Ҹ кҙҖл Ё м§Ҳнҷҳмқ„ кі л Өн•ҳм—¬ лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм••мқ„ к°ңмқёлі„лЎң кІ°м •н•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ. мқјл°ҳм ҒмңјлЎң мЈјмҡ” лӘ©н‘ңлҠ” нҳҲм••мқ„ 140/80 mmHg лҜёл§ҢмңјлЎң к°җмҶҢмӢңнӮӨлҠ” кІғмқҙл©° нҷҳмһҗмқҳ мһ„мғҒм Ғ мғҒнҷ©мғҒ к°ҖлҠҘн•ң кІҪмҡ° нҳ№мқҖ мҶҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳ лҳҗлҠ” м—ҙкіөлҮҢкІҪмғүмқҳ лі‘л Ҙмқ„ к°Җ진 нҷҳмһҗмқҳ кІҪмҡ° нҳҲм••мқ„ 130/80 mmHg мқҙн•ҳлЎң мң м§Җн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқ„ лӘ©н‘ңлЎң н•ңлӢӨ[67,68].2) мқём§Җкё°лҠҘ м Җн•ҳмҷҖ кі нҳҲм••
2) мқём§Җкё°лҠҘ м Җн•ҳмҷҖ кі нҳҲм••
кі нҳҲм••кіј мқём§Җкё°лҠҘмқҳ лі‘лҰ¬мғқлҰ¬н•ҷм Ғ м—°кҙҖ кі лҰ¬лЎңлҠ” лҮҢл°ұм§Ҳ ліҖм„ұ, лҜём„ём¶ңнҳҲ л°Ҹ м—ҙкіөлҮҢкІҪмғүмңјлЎң мқҙм–ҙм§ҖлҠ” лҢҖлҮҢмҶҢнҳҲкҙҖмқҳ лҰ¬лӘЁлҚёл§Ғмқҙ мЈјмҡ” кё°м „мңјлЎң м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲлӢӨ[69]. мӨ‘л…„кё°мқҳ кі нҳҲм••мқҖ 추нӣ„ л°ңмғқн•ҳлҠ” мқём§Җкё°лҠҘ м Җн•ҳ л°Ҹ м№ҳл§Өмқҳ мЈјмҡ” м•„нҳ•мқё м•Ңмё н•ҳмқҙлЁём№ҳл§Ө л°Ҹ нҳҲкҙҖм№ҳл§ӨмҷҖ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқҙ мһҲлӢӨ[70,71]. мөңк·јмқҳ 28,000лӘ…мқҳ нҷҳмһҗлҘј лҢҖмғҒмңјлЎң н•ң л©”нғҖ 분м„қ м—°кө¬м—җ л”°лҘҙл©ҙ кі нҳҲм•• м№ҳлЈҢлҘј нҶөн•ҙ нҸүк· мҲҳ축기/нҷ•мһҘкё°нҳҲм••мқ„ 10/4 mmHg к°җмҶҢмӢңнӮӨл©ҙ м№ҳл§Ө л°ңлі‘ мң„н—ҳлҸ„к°Җ 13% к°җмҶҢлҗҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ нҷ•мқёлҗҳм—Ҳмңјл©° мҲҳ축기нҳҲм•• 130 mmHg мқҙн•ҳлЎңмқҳ м§ҖмҶҚм Ғ кҙҖлҰ¬лҠ” лҮҢл°ұм§Ҳ ліҖм„ұмқҳ 진н–ү л°Ҹ м „л°ҳм Ғмқё мқём§Җкё°лҠҘ м Җн•ҳлҘј мӨ„мқёлӢӨлҠ” ліҙкі к°Җ мһҲлӢӨ. л”°лқјм„ң мқём§Җкё°лҠҘ м Җн•ҳ л°Ҹ м№ҳл§Өмқҳ мң„н—ҳмқ„ мӨ„мқҙкё° мң„н•ҙ мӨ‘л…„кё° л°Ҹ л…ёл…„кё°м—җ кі нҳҲм•• м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мӢңн–үн•ҳкі нҳҲм•• кҙҖлҰ¬лҘј м§ҖмҶҚм ҒмңјлЎң 추кө¬н•ҳлҠ” кІғмқ„ к¶ҢмһҘн•ңлӢӨ[72-74].
- кІ° лЎ
- кІ° лЎ
мӢ¬лҮҢнҳҲкҙҖм§Ҳнҷҳмқҳ мң„н—ҳмқ„ мӨ„мқҙкё° мң„н•ң л…ёл Ҙмқҳ мқјнҷҳмңјлЎң көӯлӮҙ нҷҳмһҗл“Өмқҳ кі нҳҲм•• м№ҳлЈҢмңЁкіј мЎ°м ҲлҘ мқ„ лҚ” лҶ’кІҢ к°ңм„ н• н•„мҡ”к°Җ мһҲмңјл©° л§Ңм„ұ м§Ҳнҷҳ нҷҳмһҗкө°мқ„ м ‘н• л№ҲлҸ„к°Җ лҶ’мқҖ мӢ кІҪкіј мқҳмӮ¬лЎңм„ң м •нҷ•н•ң нҳҲм•• мёЎм •, мң„н—ҳлҸ„ нҸүк°ҖлҘј нҶөн•ң м№ҳлЈҢ кІ°м • л°Ҹ лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм•• мҲҳлҰҪ, к°Ғ кі„м—ҙмқҳ кі нҳҲм•• м•Ҫм ңмқҳ нҠ№м„ұмқ„ нҢҢм•…н•ҳкі л¶Җмһ‘мҡ©мқ„ мӨ„мқҙкё° мң„н•ң л…ёл Ҙмқҙ 진лЈҢ мқјм„ м—җм„ң н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ. 2023л…„ мң лҹҪкі нҳҲм••н•ҷнҡҢ к°Җмқҙл“ңлқјмқёмқҳ лӮҙмҡ©мқҙ кі нҳҲм••мқҳ 분лҘҳ, лӘ©н‘ң нҳҲм•• л“ұмқҳ мёЎл©ҙм—җм„ң лӢӨмҶҢ ліөмһЎн•ҳкІҢ ліҙмқј мҲҳ мһҲмңјлӮҳ кі нҳҲм••мқҳ л“ұкёүкіј лӢЁкі„м—җ л”°лҘё мң„н—ҳкө°мқҳ 분лҘҳ, лҸҷл°ҳ м§Ҳнҷҳкіј нҷҳмһҗмқҳ мғҒнҷ©м—җ л§һлҠ” к°ңлі„м Ғмқё м№ҳлЈҢм§Җм№Ё л“ұмқҙ м ңмӢңлҗҳм–ҙ мһҲм–ҙ мһ„мғҒ нҳ„мһҘм—җм„ң н•©лҰ¬м ҒмңјлЎң мқҙмҡ©н• мҲҳ мһҲмқ„ кІғмңјлЎң мғқк°ҒлҗңлӢӨ.
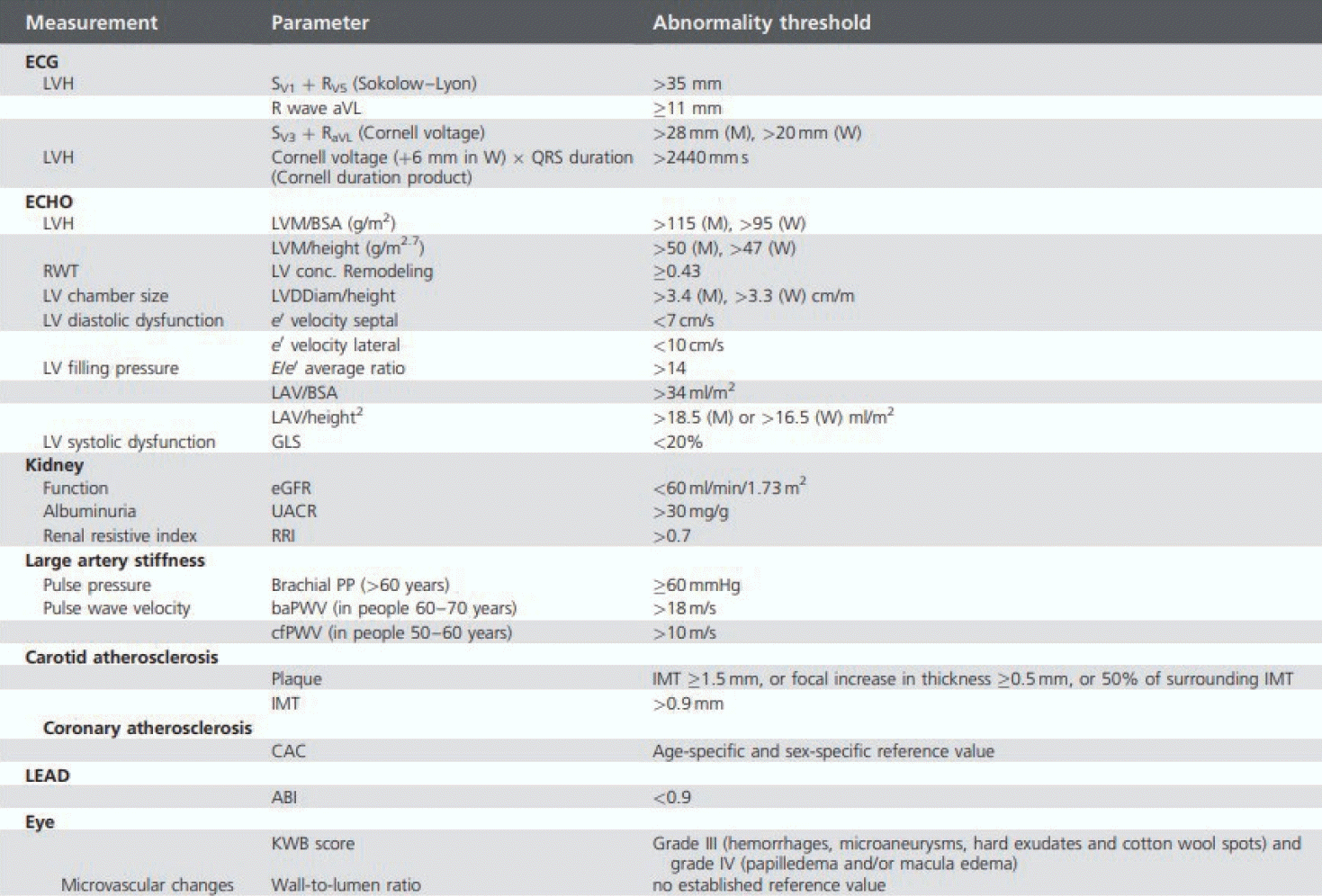
FigureВ 1.
Indicators of hypertension-mediated organ damage. Adapted from Mancia et al.6 Table 11. ECG; electrocardiogram, LVH; left ventricular hypertrophy, aVL; augmented vector left, LVM; left ventricular mass, BSA; body surface area, RWT; relative wall thickness, LV; left ventricle, LVDDiam; left ventricular diastolic diameter, LAV; left atrial volume, GLS; global longitudinal strain, eGFR; estimated glomerular filtration rate, UACR; urine albumin-creatinine ratio, RRI; renal resistive index, PP; pulse pressure, baPWV; brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity, cfPWV; carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity, IMT; imtima-media thickness, CAC; coronary artery calcium, ABI; ankle brachial pressure index, KWB; Keith-Wagener-Barker.
FigureВ 2.
Cardiovascular risk according to grade and stage of hypertension. Adapted from Mancia et al.[6] Fig. 4. HMOD; hypertension-mediated organ damage, CVD; cardiovascular disease, CKD; chronic kidney disease, BP; blood pressure, SBP; systolic blood pressure, DBP; diastolic blood pressure.

FigureВ 3.
Office blood pressure thresholds for initiating antihypertensive drug treatment. SBP; systolic blood pressure, DBP; diastolic blood pressure, CVD; cardiovascular disease, CAD; coronary artery disease, BP; blood pressure.

FigureВ 4.
Classes of antihypertensive drugs. Recommended combinations are indicated by the blue lines. ACEi; angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, ARB; angiotensin II receptor blockers, CCB; calcium channel blockers, BB; beta blockers.
FigureВ 5.
Contraindications or precautions for antihypertensive drugs. Adapted from Mancia et al.[6] Table 15. ACEi; angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, ARB; angiotensin II receptor blockers, DHP-CCB; dihydropyridine-calcium channel blockers, HFrEF; heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, AV; atrioventricular, LV; left ventricle, LVEF; left ventricular ejection fraction, CKD; chronic kidney disease, MRA; mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, eGFR; estimated glomerular filtration rate.
TableВ 1.
Definitions of hypertension
TableВ 2.
Definition of hypertension grades and stagess
- REFERENCES
- REFERENCES
- 1. Kim HC. Prevalence and management of hypertension in Korean adults. J Korean Med Assoc 2022;65:633-639.
[Article]2. Thomopoulos C, Parati G, Zanchetti A. Effects of blood-pressure-lowering treatment on outcome incidence. 12. Effects in individuals with high-normal and normal blood pressure: overview and metaanalyses of randomized trials. J Hypertens 2017;35:2150-2160.
[PubMed]3. Kim KI, Ji E, Choi JY, Kim SW, Ahn S, Kim CH. Ten-year trends of hypertension treatment and control rate in Korea. Sci Rep 2021;11:6966.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]4. Faraco G, Iadecola C. Hypertension: a harbinger of stroke and dementia. Hypertension 2013;62:810-817.
[Article] [PubMed]5. The Korean Society of Hypertension. 2022 KSH guideline: focused update of the 2018 KSH guideline. [online] [cited 2024 Jan 14]. Available from: https://www.koreanhypertension.org/reference/guide?mode=read&idno=10081.6. Mancia G, Kreutz R, Brunstrom M, Burnier M, Grassi G, Januszewicz A, et al. 2023 ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension the task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension: endorsed by the International Society of Hypertension (ISH) and the European Renal Association (ERA). J Hypertens 2023;41:1874-2071.
[PubMed]7. Ettehad D, Emdin CA, Kiran A, Anderson SG, Callender T, Emberson J, et al. Blood pressure lowering for prevention of cardiovascular disease and death: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2016;387:957-967.
[Article] [PubMed]8. Clark CE, Taylor RS, Shore AC, Ukoumunne OC, Campbell JL. Association of a difference in systolic blood pressure between arms with vascular disease and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2012;379:905-914.
[Article] [PubMed]9. Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, et al. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension 2003;42:1206-1252.
[Article] [PubMed]10. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Himmelfarb CD, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Hypertension 2018;71:e13-e115.
[PubMed]11. Stergiou GS, Palatini P, Parati G, OвҖҷBrien E, Januszewicz A, Lurbe E, et al. 2021 European Society of Hypertension practice guidelines for office and out-of-office blood pressure measurement. J Hypertens 2021;39:1293-1302.
[Article] [PubMed]12. Kallioinen N, Hill A, Horswill MS, Ward HE, Watson MO. Sources of inaccuracy in the measurement of adult patientsвҖҷ resting blood pressure in clinical settings: a systematic review. J Hypertens 2017;35:421-441.
[PubMed]13. Stergiou GS, Mukkamala R, Avolio A, Kyriakoulis KG, Mieke S, Murray A, et al. Cuffless blood pressure measuring devices: review and statement by the European Society of Hypertension Working Group on Blood Pressure Monitoring and Cardiovascular Variability. J Hypertens 2022;40:1449-1460.
[Article] [PubMed]14. National Clinical Guideline Centre (UK). Hypertension: the clinical management of primary hypertension in adults: update of clinical guidelines 18 and 34. [online] [cited 2024 Jan 14]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK83274/.15. Staessen JA, Thijs L, Fagard R, OвҖҷBrien ET, Clement D, de Leeuw PW, et al. Predicting cardiovascular risk using conventional vs ambulatory blood pressure in older patients with systolic hypertension. Systolic hypertension in Europe trial investigators. JAMA 1999;282:539-546.
[Article] [PubMed]16. Dolan E, Stanton A, Thijs L, Hinedi K, Atkins N, McClory S, et al. Superiority of ambulatory over clinic blood pressure measurement in predicting mortality: the Dublin outcome study. Hypertension 2005;46:156-161.
[Article] [PubMed]17. Ohkubo T, Imai Y, Tsuji I, Nagai K, Kato J, Kikuchi N, et al. Home blood pressure measurement has a stronger predictive power for mortality than does screening blood pressure measurement: a population-based observation in Ohasama, Japan. J Hypertens 1998;16:971-975.
[PubMed]18. Niiranen TJ, Hanninen MR, Johansson J, Reunanen A, Jula AM. Home-measured blood pressure is a stronger predictor of cardiovascular risk than office blood pressure: the Finn-Home study. Hypertension 2010;55:1346-1351.
[Article] [PubMed]19. Stergiou GS, Bliziotis IA. Home blood pressure monitoring in the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension: a systematic review. Am J Hypertens 2011;24:123-134.
[Article] [PubMed]20. Park S, Buranakitjaroen P, Chen CH, Chia YC, Divinagracia R, Hoshide S, et al. Expert panel consensus recommendations for home blood pressure monitoring in Asia: the HOPE Asia Network. J Hum Hypertens 2018;32:249-258.
[Article] [PubMed]21. Redon J, Campos C, Narciso ML, Rodicio JL, Pascual JM, Ruilope LM. Prognostic value of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in refractory hypertension: a prospective study. Hypertension 1998;31:712-718.
[Article] [PubMed]22. Kario K, Pickering TG, Umeda Y, Hoshide S, Hoshide Y, Morinari M, et al. Morning surge in blood pressure as a predictor of silent and clinical cerebrovascular disease in elderly hypertensives: a prospective study. Circulation 2003;107:1401-1406.
[Article] [PubMed]23. Mancia G, Bombelli M, Facchetti R, Madotto F, Corrao G, Trevano FQ, et al. Long-term prognostic value of blood pressure variability in the general population: results of the Pressioni Arteriose Monitorate e Loro Associazioni Study. Hypertension 2007;49:1265-1270.
[Article] [PubMed]24. Ntineri A, Niiranen TJ, McManus RJ, Lindroos A, Jula A, Schwartz C, et al. Ambulatory versus home blood pressure monitoring: frequency and determinants of blood pressure difference and diagnostic disagreement. J Hypertens 2019;37:1974-1981.
[PubMed]25. Palatini P, Saladini F, Mos L, Fania C, Mazzer A, Cozzio S, et al. Shortterm blood pressure variability outweighs average 24-h blood pressure in the prediction of cardiovascular events in hypertension of the young. J Hypertens 2019;37:1419-1426.
[Article] [PubMed]26. SCORE2 Working Group; ESC Cardiovascular Risk Collaboration. SCORE2 risk prediction algorithms: new models to estimate 10-year risk of cardiovascular disease in Europe. Eur Heart J 2021;42:2439-2454.
[PubMed] [PMC]27. SCORE2-OP Working Group; ESC Cardiovascular Risk Collaboration. SCORE2-OP risk prediction algorithms: estimating incident cardiovascular event risk in older persons in four geographical risk regions. Eur Heart J 2021;42:2455-2467.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]28. Lonnebakken MT, Izzo R, Mancusi C, Gerdts E, Losi MA, Canciello G, et al. Left ventricular hypertrophy regression during antihypertensive treatment in an outpatient clinic (the Campania Salute Network). J Am Heart Assoc 2017;6:e004152.
[PubMed] [PMC]29. Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R; Prospective Studies C. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 2002;360:1903-1913.
[Article] [PubMed]30. Lonn EM, Bosch J, Lopez-Jaramillo P, Zhu J, Liu L, Pais P, et al. Blood-pressure lowering in intermediate-risk persons without cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 2016;374:2009-2020.
[PubMed]31. Zanchetti A, Grassi G, Mancia G. When should antihypertensive drug treatment be initiated and to what levels should systolic blood pressure be lowered? A critical reappraisal. J Hypertens 2009;27:923-934.
[Article] [PubMed]32. Liu L, Zhang Y, Liu G, Li W, Zhang X, Zanchetti A, et al. The felodipine event reduction (FEVER) study: a randomized longterm placebo-controlled trial in Chinese hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 2005;23:2157-2172.
[Article] [PubMed]33. Sundstrom J, Arima H, Jackson R, Turnbull F, Rahimi K, Chalmers J, et al. Effects of blood pressure reduction in mild hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2015;162:184-191.
[Article] [PubMed]34. Arguedas JA, Leiva V, Wright JM. Blood pressure targets in adults with hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2020;12:CD004349.
[Article] [PubMed]35. Zhang W, Zhang S, Deng Y, Wu S, Ren J, Sun G, et al. Trial of intensive blood-pressure control in older patients with hypertension. N Engl J Med 2021;385:1268-1279.
[Article] [PubMed]36. Beckett NS, Peters R, Fletcher AE, Staessen JA, Liu L, Dumitrascu D, et al. Treatment of hypertension in patients 80 years of age or older. N Engl J Med 2008;358:1887-1898.
[Article] [PubMed]37. Weber MA, Julius S, Kjeldsen SE, Brunner HR, Ekman S, Hansson L, et al. Blood pressure dependent and independent effects of antihypertensive treatment on clinical events in the VALUE trial. Lancet 2004;363:2049-2051.
[Article] [PubMed]38. Williams B, Mancia G, Spiering W, Rosei EA, Azizi M, Burnier M, et al. 2018 ESC/ESH guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J 2018;39:3021-3104.
[PubMed]39. Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Himmelfarb CD, et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines. Circulation 2018;138:e426-e483.
[PubMed]40. Mancia G, Laurent S, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Burnier M, Caulfield MJ, et al. Reappraisal of European guidelines on hypertension management: a European Society of Hypertension task force document. J Hypertens 2009;27:2121-2158.
[PubMed]41. Celik T, Iyisoy A, Kursaklioglu H, Kardesoglu E, Kilic S, Turhan H, et al. Comparative effects of nebivolol and metoprolol on oxidative stress, insulin resistance, plasma adiponectin and soluble P-selectin levels in hypertensive patients. J Hypertens 2006;24:591-596.
[Article] [PubMed]42. Shimamoto K, Ando K, Fujita T, Hasebe N, Higaki J, Horiuchi M, et al. The Japanese Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension (JSH 2014). Hypertens Res 2014;37:253-390.
[Article] [PubMed]43. Leenen FH, Nwachuku CE, Black HR, Cushman WC, Davis BR, Simpson LM, et al. Clinical events in high-risk hypertensive patients randomly assigned to calcium channel blocker versus angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor in the antihypertensive and lipidlowering treatment to prevent heart attack trial. Hypertension 2006;48:374-384.
[Article] [PubMed]44. Williams B, MacDonald TM, Morant S, Webb DJ, Sever P, McInnes G, et al. Spironolactone versus placebo, bisoprolol, and doxazosin to determine the optimal treatment for drug-resistant hypertension (PATHWAY-2): a randomised, double-blind, crossover trial. Lancet 2015;386:2059-2068.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]45. Chua SK, Lai WT, Chen LC, Hung HF. The antihypertensive effects and safety of LCZ696 in patients with hypertension: a systemic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Clin Med 2021;10:2824.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]46. Roush GC, Ernst ME, Kostis JB, Tandon S, Sica DA. Head-tohead comparisons of hydrochlorothiazide with indapamide and chlorthalidone: antihypertensive and metabolic effects. Hypertension 2015;65:1041-1046.
[Article] [PubMed]47. Ishani A, Cushman WC, Leatherman SM, Lew RA, Woods P, Glassman PA, et al. Chlorthalidone vs. hydrochlorothiazide for hypertension-cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med 2022;387:2401-2410.
[Article] [PubMed]48. Roush GC, Holford TR, Guddati AK. Chlorthalidone compared with hydrochlorothiazide in reducing cardiovascular events: systematic review and network meta-analyses. Hypertension 2012;59:1110-1117.
[Article] [PubMed]49. Wajngarten M, Silva GS. Hypertension and stroke: update on treatment. Eur Cardiol 2019;14:111-115.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]50. Willey JZ, Moon YP, Kahn E, Rodriguez CJ, Rundek T, Cheung K, et al. Population attributable risks of hypertension and diabetes for cardiovascular disease and stroke in the northern Manhattan study. J Am Heart Assoc 2014;3:e001106.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]51. Moullaali TJ, Wang X, Martin RH, Shipes VB, Robinson TG, Chalmers J, et al. Blood pressure control and clinical outcomes in acute intracerebral haemorrhage: a preplanned pooled analysis of individual participant data. Lancet Neurol 2019;18:857-864.
[Article] [PubMed]52. Rodriguez-Luna D, Pineiro S, Rubiera M, Ribo M, Coscojuela P, Pagola J, et al. Impact of blood pressure changes and course on hematoma growth in acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Eur J Neurol 2013;20:1277-1283.
[Article] [PubMed]53. Hemphill JC 3rd, Greenberg SM, Anderson CS, Becker K, Bendok BR, Cushman M, et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2015;46:2032-2060.
[Article] [PubMed]54. Buletko AB, Thacker T, Cho SM, Mathew J, Thompson NR, Organek N, et al. Cerebral ischemia and deterioration with lower blood pressure target in intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2018;91:e1058-e1066.
[Article] [PubMed]55. Wang X, Di Tanna GL, Moullaali TJ, Martin RH, Shipes VB, Robinson TG, et al. J-shape relation of blood pressure reduction and outcome in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: a pooled analysis of INTERACT2 and ATACH-II individual participant data. Int J Stroke 2022;17:1129-1136.
[Article] [PubMed]56. Moullaali TJ, Wang X, Sandset EC, Woodhouse LJ, Law ZK, Arima H, et al. Early lowering of blood pressure after acute intracerebral haemorrhage: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2022;93:6-13.
[Article] [PubMed]57. Qureshi AI, Huang W, Lobanova I, Barsan WG, Hanley DF, Hsu CY, et al. Outcomes of intensive systolic blood pressure reduction in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage and excessively high initial systolic blood pressure: post hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Neurol 2020;77:1355-1365.
[Article] [PubMed]58. Tsivgoulis G, Katsanos AH, Butcher KS, Boviatsis E, Triantafyllou N, Rizos I, et al. Intensive blood pressure reduction in acute intracerebral hemorrhage: a meta-analysis. Neurology 2014;83:1523-1529.
[Article] [PubMed]59. Britton M, Carlsson A, de Faire U. Blood pressure course in patients with acute stroke and matched controls. Stroke 1986;17:861-864.
[Article] [PubMed]60. Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T, Adeoye OM, Bambakidis NC, Becker K, et al. 2018 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2018;49:e46-e110.
[PubMed]61. Ahmed N, Wahlgren N, Brainin M, Castillo J, Ford GA, Kaste M, et al. Relationship of blood pressure, antihypertensive therapy, and outcome in ischemic stroke treated with intravenous thrombolysis: retrospective analysis from safe implementation of thrombolysis in stroke-international stroke thrombolysis register (SITS-ISTR). Stroke 2009;40:2442-2449.
[Article] [PubMed]62. Wu W, Huo X, Zhao X, Liao X, Wang C, Pan Y, et al. Relationship between blood pressure and outcomes in acute ischemic stroke patients administered lytic medication in the TIMS-China study. PLoS One 2016;11:e0144260.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]63. Robinson TG, Potter JF, Ford GA, Bulpitt CJ, Chernova J, Jagger C, et al. Effects of antihypertensive treatment after acute stroke in the continue or stop post-stroke antihypertensives collaborative study (COSSACS): a prospective, randomised, open, blinded-endpoint trial. Lancet Neurol 2010;9:767-775.
[Article] [PubMed]64. Progress Collaborative Group. Randomised trial of a perindoprilbased blood-pressure-lowering regimen among 6,105 individuals with previous stroke or transient ischaemic attack. Lancet 2001;358:1033-1041.
[Article] [PubMed]65. Pats Collaborating Group. Post-stroke antihypertensive treatment study. A preliminary result. Chin Med J (Engl) 1995;108:710-717.
[PubMed]66. Lawes CM, Bennett DA, Feigin VL, Rodgers A. Blood pressure and stroke: an overview of published reviews. Stroke 2004;35:776-785.
[Article] [PubMed]67. Kernan WN, Ovbiagele B, Black HR, Bravata DM, Chimowitz MI, Ezekowitz MD, et al. Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke and transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2014;45:2160-2236.
[PubMed]68. Group SPSS, Benavente OR, Coffey CS, Conwit R, Hart RG, McClure LA, et al. Blood-pressure targets in patients with recent lacunar stroke: the SPS3 randomised trial. Lancet 2013;382:507-515.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]69. Siedlinski M, Carnevale L, Xu X, Carnevale D, Evangelou E, Caulfield MJ, et al. Genetic analyses identify brain structures related to cognitive impairment associated with elevated blood pressure. Eur Heart J 2023;44:2114-2125.
[Article] [PubMed] [PMC]70. Collaborators GBDD. Global, regional, and national burden of AlzheimerвҖҷs disease and other dementias, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2016. Lancet Neurol 2019;18:88-106.
[PubMed] [PMC]71. Collaborators GBDDF. Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: an analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Public Health 2022;7:e105-e125.
[PubMed] [PMC]72. Peters R, Xu Y, Fitzgerald O, Aung HL, Beckett N, Bulpitt C, et al. Blood pressure lowering and prevention of dementia: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Eur Heart J 2022;43:4980-4990.
[Article] [PubMed]
