일과성전체기억상실 환자에서 우연히 발견된 두정부 수막뇌탈출증
Incidentally Detected Parietal Meningoencephalocele in a Patient with Transient Global Amnesia
Article information
61세 남자가 일주일 전 발생한 5시간 동안의 기억상실로 내원하였다. 동반 증상 및 두부 외상 병력은 없었고 신경계 진찰, 간이정신상태 검사, 뇌파 검사에서 이상은 없었다. 뇌자기공명영상에서 정상 뇌와 등신호를 보이고 우측 두정엽과 연속성을 갖는 조직이 뇌척수액 영역과 함께 두개판내(intradiploic) 공간에 위치해 있었으며 우측 두정골의 결손이 관찰되었다. 확산강조영상에서는 좌측 해마에 점상 고신호강도 병변이 확인되었다(Fig.).
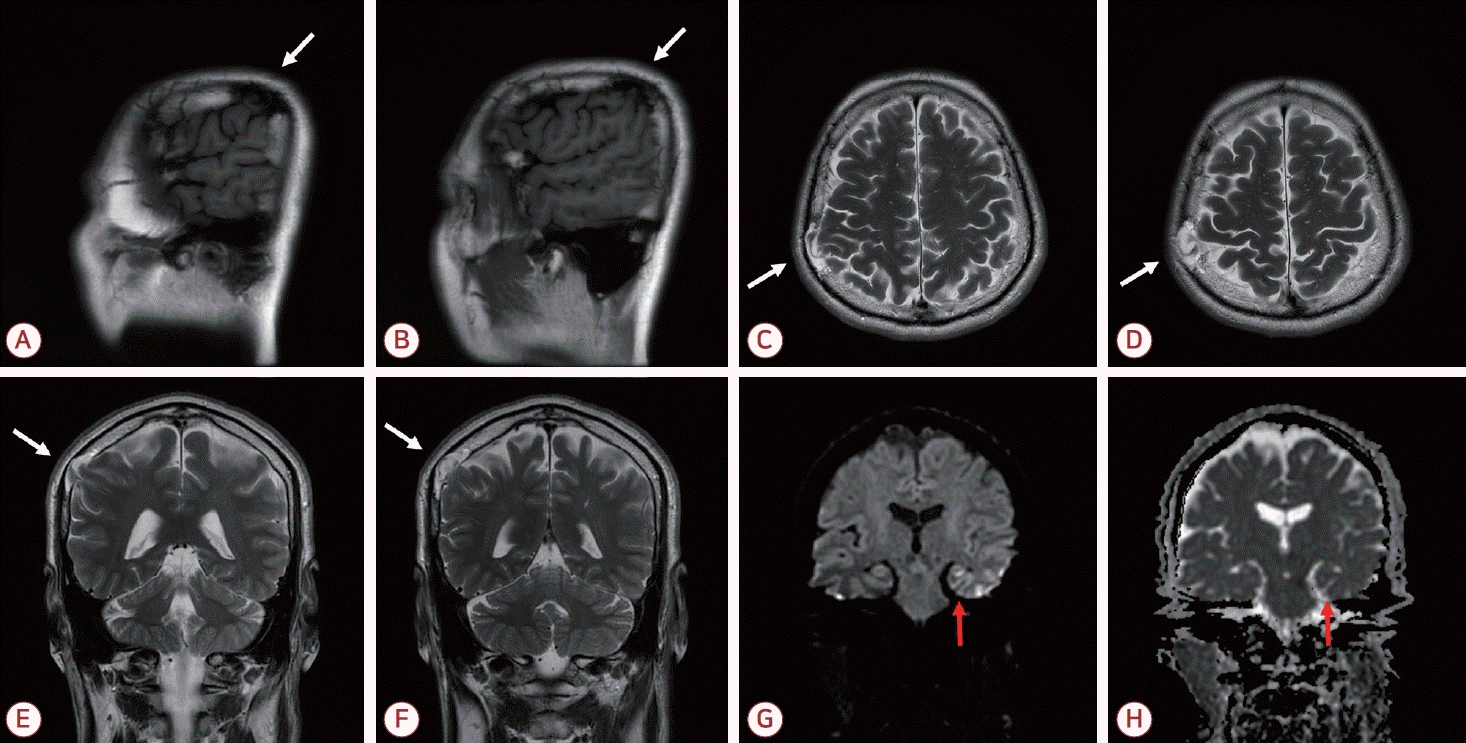
Sagittal T1-weighted image (A, B), axial T2-weighted images (C, D), coronal T2-weighted images (E, F), DWI (G), and ADC image (H) from the brain MRI. (A-F) Parenchymal tissue showing signal intensity identical to normal brain and continuous with the right parietal lobe is seen within the intradiploic space along with cerebrospinal fluid, accompanied by a defect of the right parietal bone (white arrow). (G, H) A punctate hyperintense lesion with mild ADC reduction is noted in the left hippocampus on DWI (red arrow). DWI; diffusion weighted image, ADC; apparent diffusion coefficient, MRI; magnetic resonance imaging.
수막뇌탈출증은 두개골 결손을 통해 뇌 조직과 뇌막이 탈출하는 상태를 말하며 후두부에 흔히 발생한다[1]. 이는 선천적 또는 후천적으로 발생할 수 있는데 선천적인 경우 보통 정중선에서 발생하고 내외판 모두가 결손되며 동반 기형이 있는 경우가 많다[2].
두개판내(intradiploic) 수막뇌탈출증은 두개골의 경막과 내판만 결손되고 외판은 보존되어 뇌조직이 두 판 사이의 공간으로 탈출한 것을 말한다[3]. 이 경우 무증상인 경우가 많아 대부분 우연히 발견되나 발작, 감각 저하, 편마비, 두통 등의 증상을 동반하기도 한다. 현재 널리 받아들여지는 병인은 둔상으로 골절된 내판이 수축하며 발생한 음압에 의하여 뇌조직과 뇌척수액이 두 판 사이 공간으로 탈출한다는 것이다[1]. 외판이 보존된 본 증례 환자의 병변은 모종의 경미한 외상 후 발생한 후천성 병변일 것으로 사료된다. 일과성전체기억상실은 해마의 일시적 기능 저하가, 수막뇌탈출증에서 보고된 증상은 탈출된 뇌조직이 담당하는 기능 이상이 주요 병태생리이므로 두 질환의 상호 연관성은 낮을 것으로 판단하였다.
국내 두정부 수막뇌탈출증 보고는 두 건뿐이며 모두 간헐적 두통으로 내원한 환자에서 우연히 발견된 사례였다[2,3]. 본 증례는 일과성전체기억상실 환자에서 우연히 발견된 두정부 수막뇌탈출증의 드문 증례이다.