삼킴곤란을 유발하는 거대전방경추골극
Giant Anterior Cervical Osteophyte Causing Dysphagia
Article information
69세 환자가 수년 전부터 진행하는 삼킴곤란으로 내원하였다. 30년 전 좌측 기저핵의 뇌내출혈로 경한 구음장애와 우측 근력 Medical Research Council 척도 4등급이었다. 삼킴곤란은 액체류에서도 있었으나 고체류에서 더 심하였다. 혀의 움직임이나 다른 신경계증상의 악화는 없었고, 뇌 자기공명영상에서 새로운 병변은 없었다(Fig. A). 비디오투시연하검사에서 구강통과시간 연장 및 인두기에서 후두거상, 후두개 후방경사 저하가 있었으며 경추의 전방골극이 관찰되었다. 경추 X선검사, 경추 CT에서 경추 2-6번 부위의 전방골극과 전종인대골화증으로 인한 인두와 식도의 압박이 확인되었다(Fig. B). 경추 2-4번 부위의 골극을 수술로 제거 후 삼킴곤란은 일부 호전되었다(Fig. C).
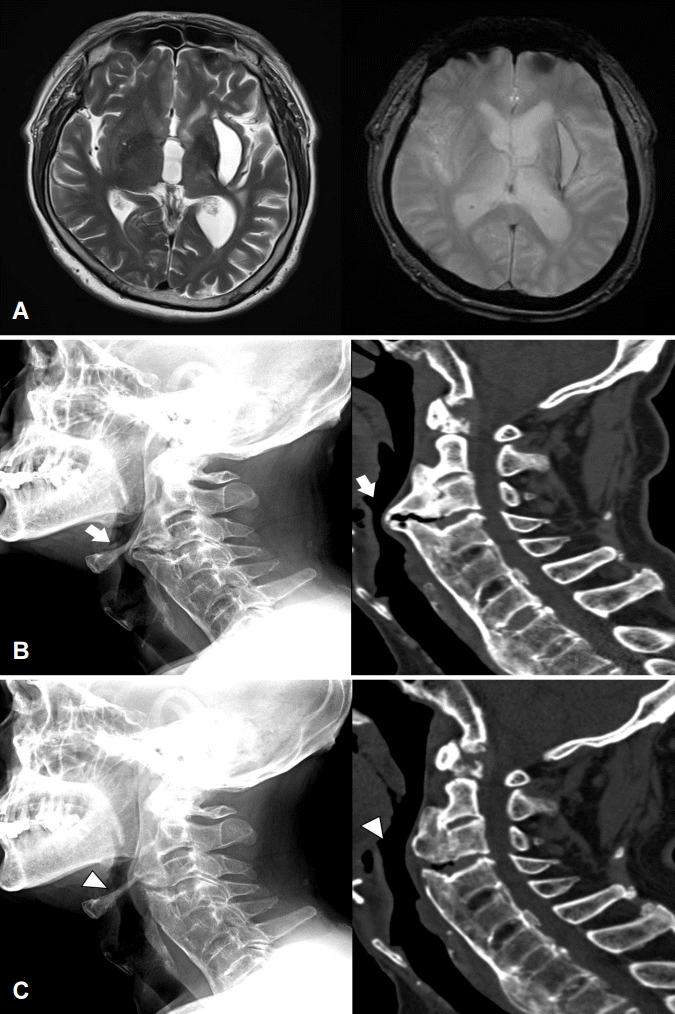
(A) Brain magnetic resonance imaging shows old left basal ganglia hemorrhage on T2-weighted image and T2-weighted gradient echo image. (B) Preoperative cervical spine X-ray and computed tomography scan reveal giant cervical anterior osteophyte at C2-6 vertebral bodies and ossification of anterior longitudinal ligament causing compression of posterior pharyngeal wall (arrows). (C) Postoperative images show partial resection of the anterior osteophyte at C2-4 and decompression of pharyngoesophageal tract (arrowheads).
삼킴곤란을 호소하는 환자에서 다른 신경계증상이 동반되거나 악화되지 않은 경우 구조적 원인에 의한 것일 수 있다. 경추골극 및 전종인대의 석회화로 인한 압박도 삼킴곤란을 유발할 수 있으므로 주의가 필요하다[1,2].