뇌졸중으로 오인된 축삭구형체를 동반한 유전미만백질뇌병증 환자 증례
Hereditary Diffuse Leukoencephalopathy with Axonal Spheroids Mistaken for Stroke: A Case Report
Article information
Trans Abstract
Hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids (HDLS) is a rare autosomal dominant disorder that is caused by colony stimulating factor 1 receptor gene mutation degenerating the cerebral white matter. It is characterized by various symptoms such as progressive cognitive decline, personality changes, and motor disorders. Since these clinical features are not consistent, HDLS is often underdiagnosed or misdiagnosed. This case report presents a patient priorly diagnosed with cerebral infarction by clinical features, but eventually with HDLS by a genetic test.
축삭구형체를 동반한 유전미만백질뇌병증(hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids, HDLS)은 상염색체 우성으로 유전되며, colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R)유전자 돌연변이에 의해 뇌 백질 퇴행이 발생하는 드문 질환이다[1]. HDLS의 임상 증상은 성격 변화, 치매, 파킨슨증, 보행장애 등과 같이 매우 다양하게 나타난다[2]. 뇌 자기공명영상(magnetic resonance imaging, MRI)에서는 T2강조영상과 액체감쇠역전회복(fluid attenuated inversion recovery, FLAIR)영상에서 양측 전두엽 또는 전두두정엽 피질하와 뇌실주위의 백질에서 고신호강도가 특징적으로 나타나지만, 초기에는 비대칭적으로 나타나거나 병변이 없을 수도 있다[1]. 이 질환에 대한 국내 보고는 많지 않으며, 다양한 임상 증상과 비전형적인 뇌 영상 소견으로 진단에 어려움이 많다[2-4]. 저자들은 뇌경색 증상으로 오인한 후 추가적으로 시행한 유전자검사를 통해 HDLS로 진단된 환자를 경험하여 보고하고자 한다.
증 례
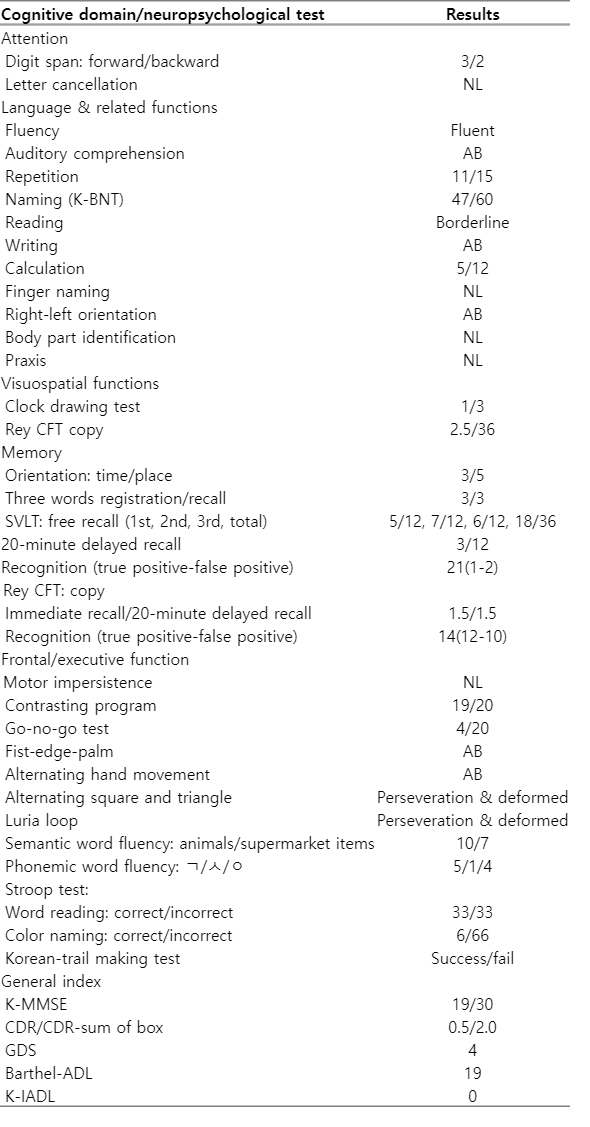
대졸의 14년 학력의 52세 남자가 약 3개월 전 업무 중 갑자기 발생하여 악화 없이 지속된 구음장애와 우측 상지 어둔함으로 신경과 뇌혈관센터에 왔다. 환자는 당뇨병과 이상지질혈증의 과거력으로 약물을 복용 중이었고, 음주력과 흡연력은 없었다. 가족력에서 아버지는 다른 원인으로 뇌 MRI를 시행한 후 무증상 뇌경색을 진단받았으며 내원 전 사망한 상태였고, 어머니는 당뇨병이 있었다(Fig. 1). 신경계진찰에서 구음장애가 관찰되었지만 양측 상하지 근력은 정상이었다. 감각기능검사와 소뇌기능검사, 보행 모두 정상이었다. 심부건반사는 정상이었고, 병적반사는 없었다. 당시 갑작스러운 신경계증상 발생으로 뇌경색과 같은 뇌혈관성 질환을 감별하기 위해 뇌 MRI를 실시하였다. 확산강조영상(diffusion weighted image, DWI)의 우측 두정엽에서 국소확산제한 병변이 관찰되었고(Fig. 2-A), FLAIR 영상과 T1강조영상의 좌측 난형중심(central semiovale)부위에서 만성 열공뇌경색(lacuna infarction)의심 소견이 관찰되었다(Fig. 2-B, C). 또한 FLAIR 영상에서는 양측 전두엽과 두정엽의 뇌실주위 백질에서 고음영과 뇌위축이 관찰되었다(Fig. 2B, D, E). 환자는 만성 열공뇌경색과 우연히 발견된 급성뇌경색으로 진단된 이후 약물 치료를 하며 경과 관찰하였다. 하지만 그 해 말부터 30년 이상 계산을 주업무로 근무하던 환자가 점차 계산 실수가 잦아 퇴사 권고를 받았고, 1년 뒤부터는 운전 중 차선을 잘 지키지 못해 접촉사고가 잦아지기 시작하였다. 증상 발생 2년 후 좁은 보폭으로 걷기 시작하면서 알아듣기 힘들 정도의 말더듬과 인지저하로 치매 클리닉으로 의뢰되었다. 신경계진찰에서 문장의 20% 이상의 음절 반복으로 인해 알아듣기 힘든 말더듬이 관찰되었다. 상하지 근력 및 감각기능검사는 정상이었지만, 우측 상하지에서 굴근경직(flexor spasticity)이 경하게(modified Ashworth Scale grade 1) 관찰되었고 경축(rigidity)은 없었다. 또한 좌측 상지에서 활동떨림이 나타났다. 보행을 할 때 보폭이 줄어 종종걸음이 관찰되었고, 우측 상지 흔들림이 감소되어 있었다. 제자리 돌기를 할 때 주저함과 통나무 도는(en bloc)듯한 모습이 관찰되었다. 소뇌 기능검사에서는 양측에서 상반운동반복장애(dysdiadochokinesia)가 관찰되는 것 이외는 정상이었다. 피질감각기능검사는 모두 정상이었으나 양측에서 사지 관념운동실행증이 나타났으며, 특히 좌측이 심했다. 실서증, 계산장애, 손가락실인증과 좌우 혼동 모두 나타나 Gerstmann 증후군도 관찰되었다. 우측 상하지에서 심부건반사가 감소하였고, 병적반사는 없었다. 내원 후 시행한 첫 서울신경 심리선별종합검사에서 모든 영역이 0.01%ile 이하로 심한 인지기능 저하가 확인되었고, 간이정신상태검사(mini mental status examination, MMSE)의 점수는 19점, 임상치매평가척도(clinical dementia rating, CDR)의 점수는 0.5점, 박스총점(Sum of Boxes, CDR-SB)은 2.0점이었다(Table 1). 도구일상활동 점수는 정상이었다. 추적 관찰한 뇌 MRI의 DWI에서 초기에 관찰되었던 우측 두정엽의 국소확산제한 병변이 그대로 확인되었다(Fig. 2-F). FLAIR 영상에서 열공뇌경색은 관찰되지 않았지만 뇌실주위 백질의 고신호강도 병변은 더 진행하였고, 양측 전두엽과 두정엽의 위축이 현저하게 악화되었다(Fig. 2-G-I). T1강조시상영상에서 뇌량의 위축도 확인되었다(Fig. 2-J). 전혈구검사, 간기능검사, 갑상샘기능검사, 비타민 B12, 매독선별검사, 자가면역질환감별검사를 포함하는 모든 혈액 검사는 정상이었다. 뇌파검사와 F-18 FP-CIT뇌양전자방출단층촬영에서도 이상 소견은 없었다. 아포지단백질 E (apolipoprotein E) 유전자아형은 ε3/ε3였고, 18F-flutemetamol 아밀로이드양성자단층 촬영에서 아밀로이드 축적은 관찰되지 않았다. 첫 증상 발생 3년 후 시행한 CSF1R (NM_005211.3) 유전자검사에서 18번째 엑손에서 c.2381T>C (p.Ile794Thr) 이형접합자 돌연변이가 확인되어 HDLS로 확진되었다. 이후 환자는 말더듬과 인지저하, 실행증, 보행장애가 더욱 악화되어 대화가 불가능해졌으며, 보행을 포함한 모든 일상생활이 혼자서는 불가능해졌다. MMSE의 점수는 1년 전과 비교하여 4점 저하된 15점, CDR 점수 1점, CDR-SB의 점수 8점이었다.
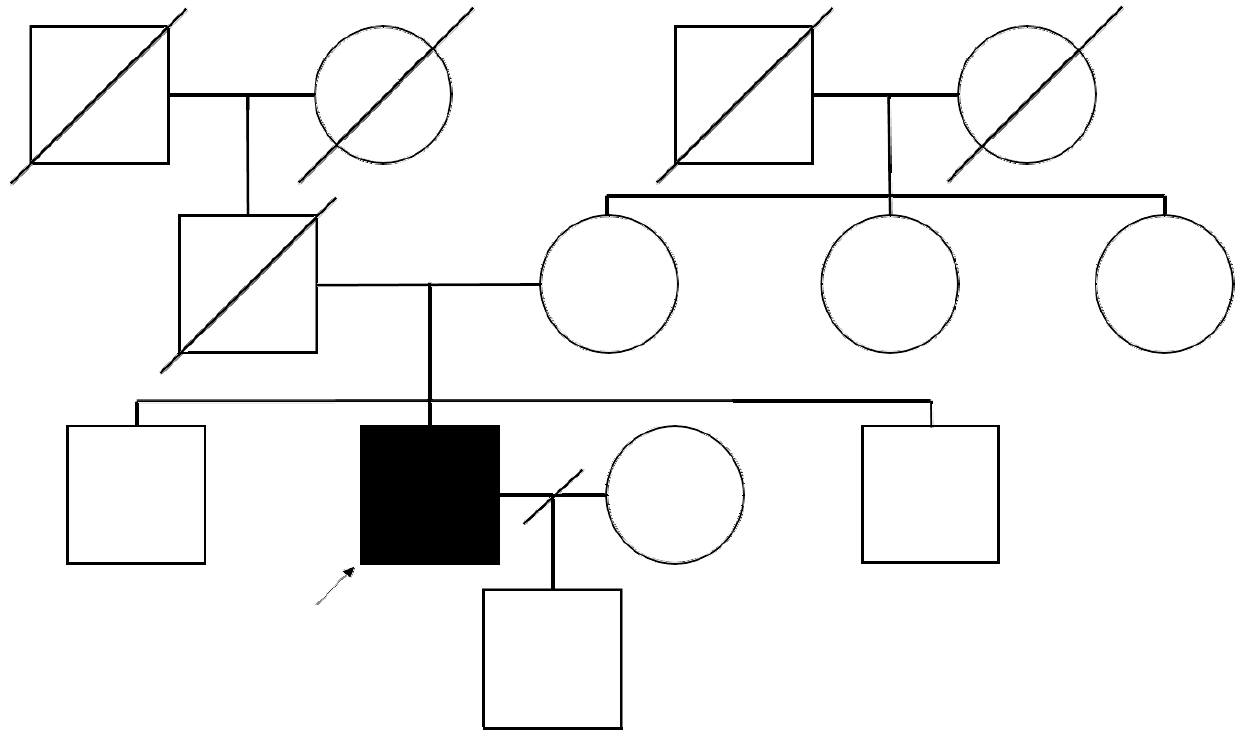
Pedigrees of the patient. An arrow and darkened symbol indicate the proband. Squares and circles represent males and females, respectively. A diagonal line through a symbol means decease.

Brain images of hereditary diffuse leukoencephalopathy with axonal spheroids. (A) Focal diffusion restriction lesion is observed in the right high parietal lobe. Hyperintense signal on initial FLAIR image (B) and hypointense signal on T1 weighted image (yellow arrow) (C) are suspicious of lacunar infarction (yellow arrow). (D, E) Initial FLAIR hyperintense signal alterations in both central semiovale and periventricular white matter are seen. (F) In the follow-up DWI, there is no change of focal diffusion hyperintensity in the right high parietal lobe after 3 years. (G-I) The follow-up FLAIR images reveal more extended and aggravated periventricular white matter hyperintensities and diffuse cortical atrophy after 3 years. (J) T1 sagittal image shows diffuse atrophy in the corpus callosum. FLAIR; fluid attenuated inversion recovery, DWI; diffusion weighted image.
고 찰
백질뇌병증은 감별진단이 매우 광범위하며, 진단을 위해서는 생화학적, 유전적, 신경병리적 진단이 필요하기 때문에 어려움이 있다. 특히 HDLS는 CSF1R유전자 돌연변이를 확인하거나 병리적으로 진단해야 하기 때문에 실제 임상에서는 하시모토뇌병증, 초로기알츠하이머병치매, 카다실(cerebral autosomal-dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy), 다발경화증, 뇌경색, 다른 신경퇴행질환 등으로 잘못 진단되기도 한다[2]. 본 증례도 질병 초기에 구음장애와 우측 상지 어둔함으로 내원하여 뇌경색으로 진단되었다가 이후 말더듬과 인지기능저하, 보행장애가 나타나면서 추가적으로 진행한 혈액검사, 뇌 영상검사, 유전자검사에서CSF1R유전자 돌연변이가 발견되어 HDLS로 확진되었다. 환자는 CSF1R유전자검사에서 18번째 엑손에서 c.2381T>C(p.Ile794Thr) 이형접합자 돌연변이가 확인되었으며, 이는 전 세계적으로 가장 흔하게 보고되고 있는 돌연변이다[5]. Ile794Thr돌연변이가 보고된 한 사례에서는 무증상이면서 경도의 백질 고신호강도의 뇌 MRI 소견을 보였으며, 다른 사례에서는 성격 변화 및 무감동 증상과 함께 뇌 MRI에서 광범위한 백질 고신호강도와 심한 뇌량의 위축을 보고하였다[6]. 같은 돌연변이를 가진 본 증례의 환자의 경우, 심한 말더듬과 보행장애 등 다양한 증상을 보이면서, 뇌 MRI에서 중등도의 백질 고신호강도를 보인다는 점에서 같은 Ile794Thr돌연변이를 가지더라도 임상 증상 및 뇌 MRI 소견이 다양한 표현형이질성(heterogeneity)이 흔함을 알 수 있다.
유전자검사 및 병리 진단 이외 다양한 임상 증상과 뇌 영상 소견만으로도 진단의 민감도를 높이기 위해 최근 5개 기관의 연구자 그룹에서 진단기준을 제시하였다. HDLS의 진단기준에 따르면 1) 60세 미만, 2) 빠르게 진행하는 경과의 인지저하 혹은 정신과 증상, 피라미드징후, 파킨슨증, 뇌전증 중 2가지 이상, 3) 상염색체우성 유전 혹은 산발 발생, 4) 뇌 영상 소견에서 양측 대뇌 백질 이상 혹은 뇌량의 위축, 이 중 2), 3), 4)의 만족과 함께 CSF1R돌연변이가 발견되면 확진될 수 있으며, 1)-5) 만족되지만 유전자검사가 진행되지 않았다면 추정 진단을 내릴 수 있다[7]. 따라서 본 환자의 경우 모든 항목을 충족하고 유전자검사로 돌연변이도 확인을 하였기 때문에 HDLS로 확진할 수 있었다. 하지만 만약 유전자검사를 시행하지 않았더라도 상기 진단기준에 따라 추정 진단을 내릴 수 있다.
질환의 초기 뇌 MRI에서는 양측 전두엽 혹은 전두두정엽 백질의 국소고신호강도와 같은 경미한 병변을 보일 수 있다. 질환이 진행될 수록 양측 백질 전반으로 고신호강도의 진행 및 뇌량의 위축을 특징으로 하며, U-섬유는 일반적으로 보존되고 조영증강 병변은 뚜렷하지 않다. 뇌의 위축은 주로 백질 변화가 일어나는 엽에 나타나며, 후두엽과 측두엽은 질환이 진행된 이후에 나타난다[1]. 본 증례의 경우, 초기 뇌 MRI에서 나이에 비해 전반적인 뇌위축이 심하다는 점, 양측 전두두정엽 부위 백질에서 상대적으로 고신호 강도가 대칭적인 소견을 보인다는 점 그리고 뚜렷한 열공뇌경색이 하나도 관찰되지 않는다는 점에서 대사, 독성, 염증, 감염 및 자가 면역 백질뇌병증 등도 감별진단해 볼 필요가 있다. 또한 가족력은 없지만 카다실과 같은 혈관 백질뇌병증 혹은 Late-onset metachromatic leukodystrophy, alexander disease 등과 같은 유전백질 뇌병증 등도 함께 고려해 볼 필요가 있다[8]. 2년 후 시행한 추적 검사의 DWI에서 지속적으로 국소확산제한 병변이 관찰되었는데, 이 병변은 현재까지도 정확한 기전이 밝혀지진 않았지만 설명 가능한 기전으로 1) 흥분독성 기전에 따른 세포독성부종에 의한 가능성[9] 혹은 2) 신경퇴행부위의 수초내부종(intramyelinic edema)을 반영한다는 가능성[10]들을 생각해 볼 수 있다. 특히 후자의 가능성은 일정 기간 만성적으로 이 소견을 지속하기 때문에 질환의 초기에 활용할 수 있는 특징적인 진단적 단서가 될 수 있다.
본 증례의 환자는 가족력이 전혀 없지만, 유전자돌연변이가 발견되어 HDLS가 진단되었다. HDLS는 상염색체우성유전이지만 이와 같이 가족력이 없는 경우도 적지 않다[6]. 그렇기 때문에 다양한 임상 증상과 비전형적인 뇌 영상 소견만으로는 HDLS를 진단하기에 매우 어렵다. 따라서 가족력이 없더라도 여러 증상들과 함께 증상이 진행한다면 다양한 감별진단을 고려하여야 하며, 주기적인 뇌 MRI의 추적 관찰 및 유전자검사를 통해 HDLS도 감별해 볼 필요가 있다. 그럼으로써 HDLS 환자를 조기에 진단하여 적절한 치료적 접근뿐만 아니라 가족 유전 상담을 제공할 수 있도록 해야 한다. 저자들은 구음장애와 우측 상지 위약감으로 내원하여 뇌경색으로 오인한 HDLS 환자를 경험하였기에 이를 보고하는 바이다.