비케톤고혈당유발발작에서 자기공명영상과 자기공명분광
Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Findings in Non-Ketotic Hyperglycemia-Induced Seizures
Article information
29세 남자가 3주 전부터 발생한 발작으로 왔다. 좌측 시야의 반짝거림으로 시작해 멍해지는 발작이 반복적으로 발생하였으며, 좌측 동측반맹이 보였다. 혈당 362 mg/dL, 당화혈색소 14.6%였고 뇌 magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)에서 비케톤고혈당유발발작에서 관찰되는 소견이 있었다(Fig. 1) [1]. 자기공명분광(magnetic resonance [MR] spectroscopy)에서는 젖산 증가와 N-아세틸아스파트산(N-acetyl aspartate, NAA) 감소를 보였다(Fig. 2). 항뇌전증제 사용 없이 혈당 조절 만으로 경련은 즉시 호전되었으며 좌측 반맹은 2주 후 호전되었다.
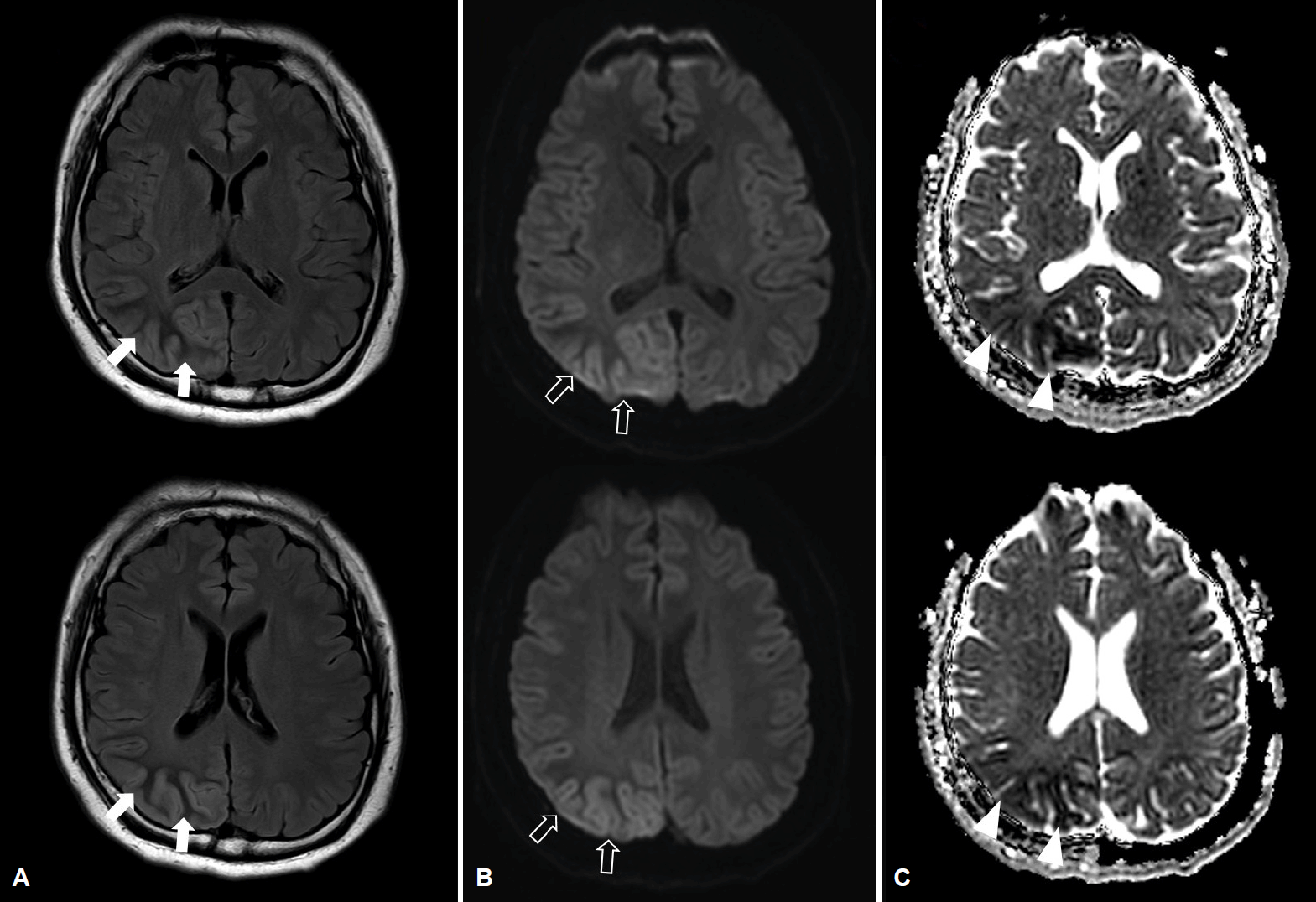
Brain magnetic resonance images. (A) FLAIR images show the subcortical hypointensity in the right occipital area (arrows) with overlying cortical hyperintensity and gyral swelling. (B) Diffusion-weighted images show cortical high signal intensity (empty arrows) and (C) the ADC maps show low signal intensity in the corresponding area. (arrowheads). FLAIR; fluid attenuated inversion recovery, ADC; apparent diffusion coefficient.
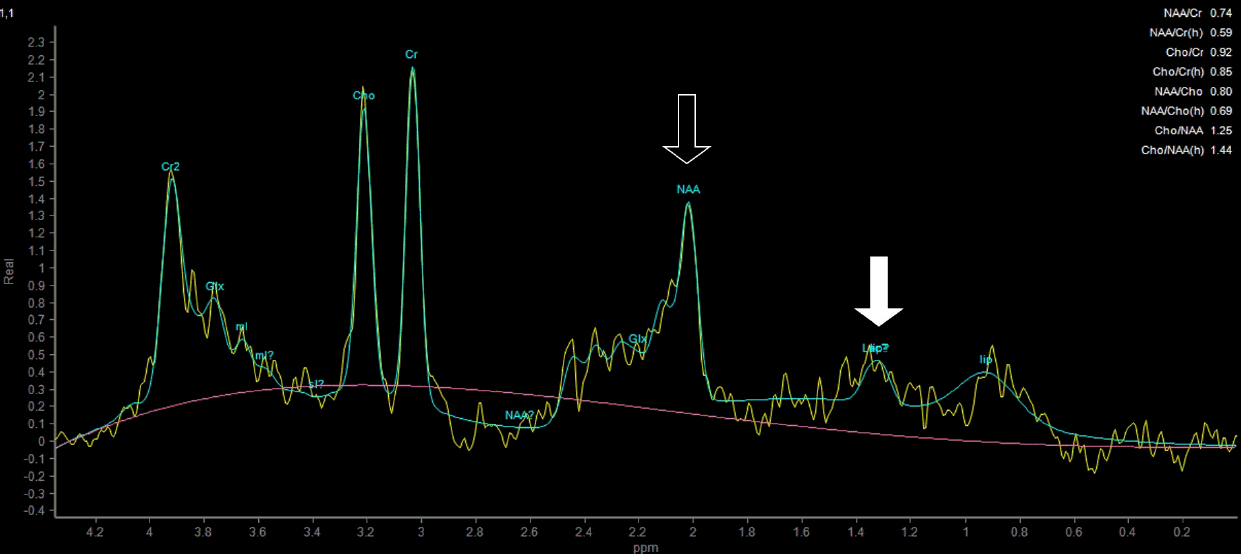
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy shows increased lactate (arrow), decreased N-acetyl aspartate (NAA) level (empty arrow), and decreased ratio of NAA/Cr (0.74) in the right occipital lobe.
비케톤성고혈당유발발작에서 특징적인 MRI 소견이 보이지만 병태생리 기전에 대해서는 정확히 알려져 있지 않다[1]. 환자의 MR spectroscopy를 고려하면 포도당 대사 장애로 인해 무산소대사의 표지자인 젖산이 증가하여 뇌실질 내 축적된 것이 반영되었을 가능성, 또는 반복적인 발작으로 인한 국소 뇌조직의 허혈성 변화에 의한 소견일 수 있다[2].