경미한 두부 손상에 의한 조영증강 액체감쇠역전회복영상에서 관찰되는 외상성 뇌막조영증강
Traumatic Meningeal Enhancement on Post-Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery after Minor Head Trauma
Article information
75세 여자가 척추관협착증으로 꼬리차단마취 후 가역적뇌혈관수축증후군 진단 하에 경과 관찰 중 침대에서 낙상하였고 당시에 의식소실 및 신경계 장애는 없었으나 좌측 후두부 부종이 관찰되었다. 뇌 컴퓨터단층검사에서 좌측 후두부 두피하 출혈 외에 이상 소견은 없었다(Fig. A). 낙상 후 3일째 시행한 액체감쇠역전회복영상에서 우측 전두엽, 좌측 후두엽과 대뇌반구 사이 뇌막에서 미세한 고신호강도 병변이 관찰되었고 이 병변은 뚜렷하게 조영증강되었으나 동시에 시행된 자화강조영상과 조영증강 T1강조영상 및 낙상 이전에 시행한 조영증강 액체감쇠역전회복영상에서는 명확한 이상이 관찰되지 않았다(Fig. B-F). 외상성 뇌 손상 후 조영증강 액체감쇠역전회복영상에서 뇌막의 조영증강 현상은 다른 영상검사에 비하여 더 흔하게 관찰되는 이상 소견으로 보고되었다[1,2]. 조영증강 액체감쇠역전회복영상은 일반적으로 시행되는 자기공명영상 기법은 아니지만 경미한 두부 외상에서 진단적 유용성이 있을 것으로 생각된다.
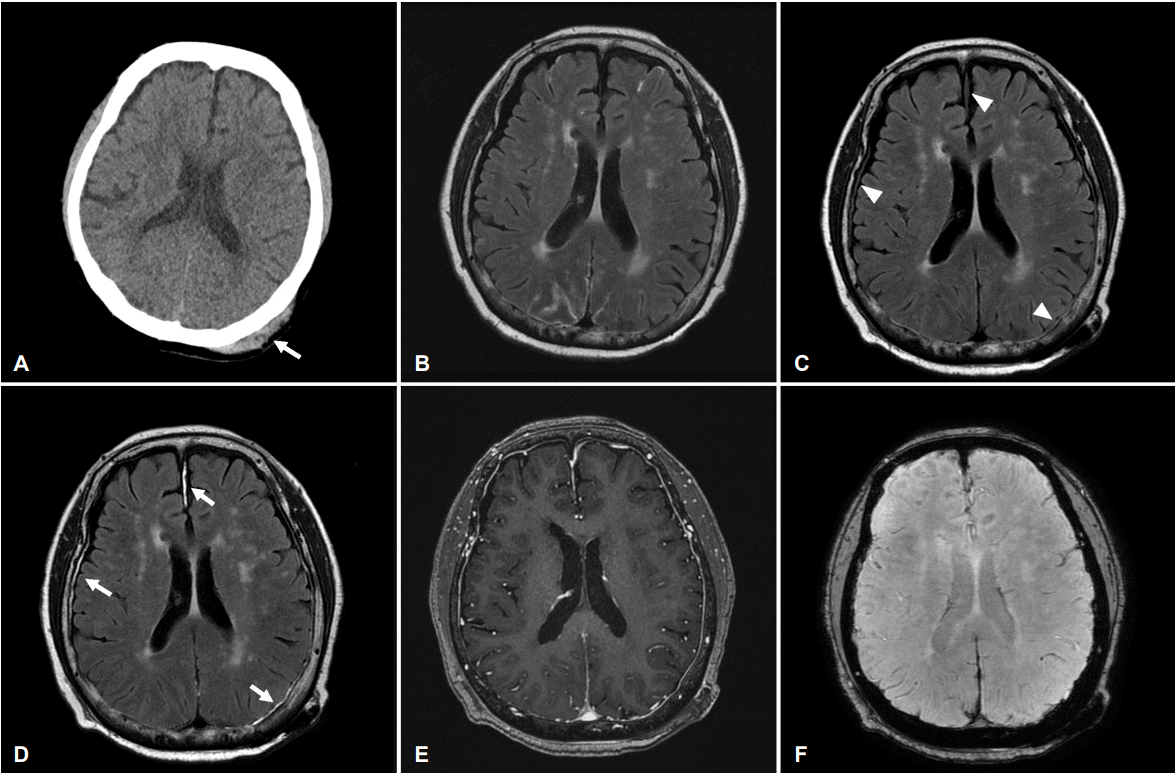
Brain CT and magnetic resonance images. (A) Brain CT shows no intracranial hemorrhage and skull fracture. Scalp hematoma (arrow) on left occipital area is noted. (B) There is no meningeal lesion on Gadolinium enhanced FLAIR image before the head trauma. (C, D) There are subtle high signal intensity meningeal lesions on FLAIR (arrowheads). Gadolinium enhanced FLAIR image shows meningeal enhancement on the left frontal, right occipital and interhemispheric fissure (arrows). (E, F) Contrast-enhanced T1 weighted image and susceptibility weighted image show no abnormal enhancement and hemorrhage. CT; computed tomography, FLAIR; fluid attenuated inversion recovery.